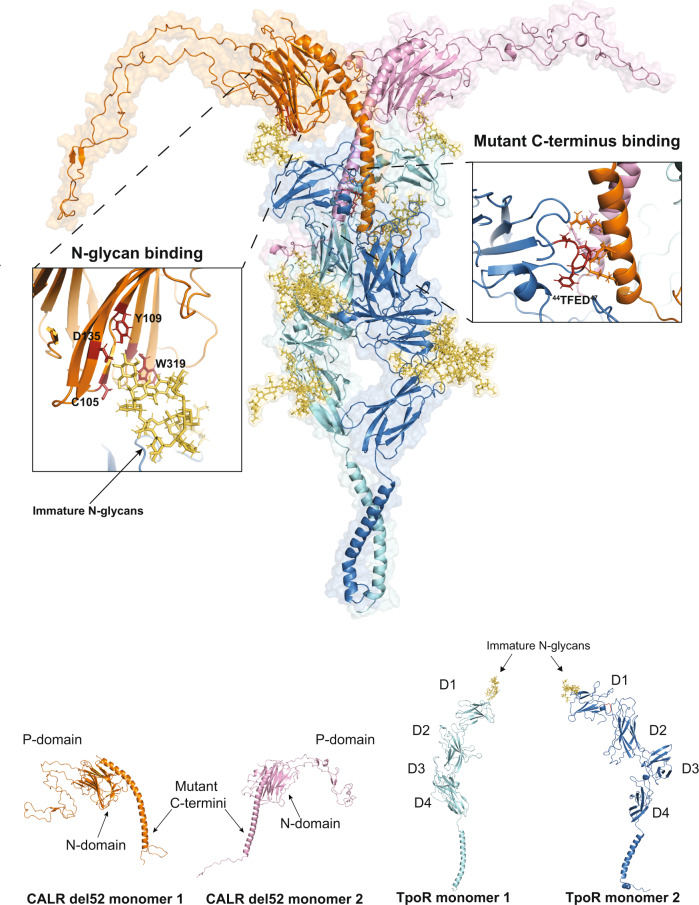
Fig. 6. Comprehensive model of the TpoR-CALR mutant complex.
Molecular dynamics of the CALR del52-TpoR tetrameric complex. The structure represents the last frame of one out of three replicates of 100 ns unconstrained MD of the CALR del52-TpoR tetrameric complex. All replicates are shown in Supplementary Fig. 15. The model illustrates how CALR mutant interacts with TpoR via two distinct regions. One region concerns the interaction between CALR N-domain (N-glycan binding domain) and immature N-glycans attached to Asn117 of TpoR. The second region involves binding of CALR mutant C-terminus to acidic patches on TpoR ECD. The interaction between TpoR negative residues and CALR mutant C-terminus may possibly occur both in cis (with the same molecule of CALR mutant with which TpoR interacts via N-glycans) or in trans. The binding between specific residues of CALR N-domain and immature N-glycans attached to Asn117 and that of the 44TFED47 motif of TpoR to CALR mutant C-termini is illustrated. The contact list of interactions detected during MD triplicate runs is provided as Supplementary data 1. TpoR molecules are shown in cyan and dark blue. CALR del52 molecules are shown in orange and pink. Key residues of CALR del52 N-domain involved in binding of immature N-glycans are shown in dark red. The 44TFED47 motif of TpoR D1 domain that interacts with CALR del52 C-termini is shown in red. The different domains of CALR mutant and TpoR are indicated.