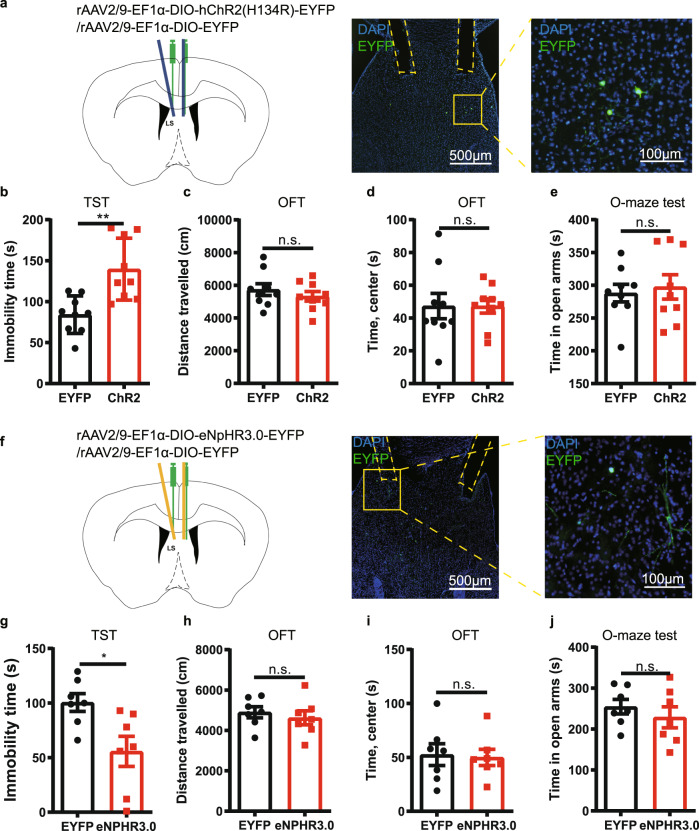
Fig. 4. Optogenetic modulation of the activity of A2AR+ neurons in the lateral septum (LS) influences depressive-like phenotype.
a Left: Schematic illustration of the location of virus injection and optic fibers implantation in A2AR-Cre mice. Right: A representative fluorescent image showing the ChR2-positive neurons (green) and the localization of the optic fibers. Nuclei are stained with DAPI in blue. Scale bar: 500/100 μm. (b-e) Optogenetic activation of LS-A2AR+ neurons increased the immobility time in the tail suspension test (TST) (n = 9 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.0017, t(16) = 3.7710) b without affecting the total distance traveled (n = 9 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.3980, t(16) = 0.8684) c or the time in the central area in the open field test (OFT) (n = 9 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.9980, t(16) = 0.002512) d and in the elevated O-maze test (n = 9 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.6868, t(16) = 0.4106) (e). f Left: Schematic illustration of the location of virus injection and optic fibers implantation in A2AR-Cre mice. Right: A representative fluorescent image shows the eNpHR3.0 positive neurons (green) and the localization of the optic fibers. Nuclei are stained with DAPI in blue. Scale bars: 500/100 μm. Optogenetic suppression of the activity of LS A2AR+ neurons decrease the immobility time in the TST (n = 7 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.0159, t(12) = 2.804) (g), without affecting the total movement distance in the OFT (n = 7 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.5465, t(12) = 0.6205) (h), the time spending in the central area in the OFT(n = 7 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.8404, t(12) = 0.2058) (i), and the duration in the open arm of the elevated O-maze (j) (n = 7 mice/group, Unpaired t test, p = 0.4188, t(12) = 0.8373). Data were shown as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01; n.s., no significant difference. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.