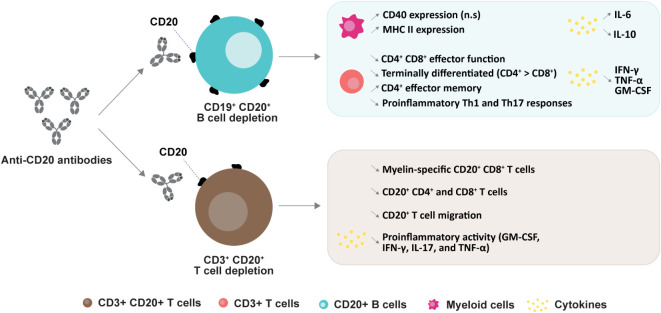
Figure 3.
Anti-CD20 mediated changes in subtypes and their functions. CD20+ B cell depletion leads to an increase in CD40 expression (n.s: non-significant) and MHC II expression in myeloid cells (79); a decrease in CD4+ and CD8+ effector function (79), proinflammatory Th1 and Th17 responses (82), and numbers of terminally differentiated T cells, and an increase in CD4+ effector memory cells (85). Secretion of cytokines are changed upon B cell deletion (79, 85). CD20+ T cell depletion induces a decrease in myelin-specific CD20+ CD8+ cells (84), in both CD20+ CD4+ and CD8+ cells (86), in CD20+ T cell migration (85) and a decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines (49, 87).