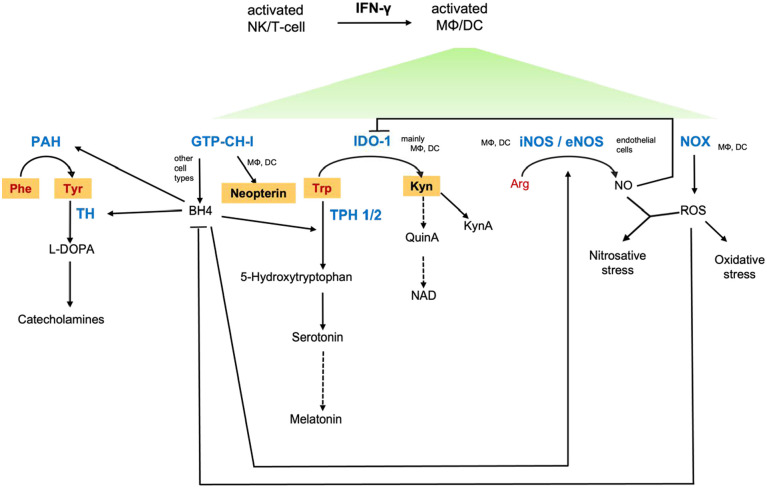
Figure 1.
Interferon gamma (IFN-γ)-dependent and related biochemical pathways. Inflammatory cascades stimulate immunobiochemical pathways, with IFN-γ being the main activating cytokine of neopterin formation via GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (GTP-CH-I) and tryptophan (Trp) catabolism along the kynurenine (Kyn) axis via indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1) in human macrophages (MΦ) and dendritic cells (DC). The shift toward neopterin production runs at the expense of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) in these cell types. BH4 is crucial for the functioning of several monoxygenases, for example phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase (PAH), tyrosine 3-monooxygenase (TH), tryptophan 5-monooxygenases (TPH), and nitric oxide synthases (NOS). Though BH4 is synthetized by other cell types, too, it is oxidation labile and availabilities may become limiting. In addition, a prooxidative milieu leads to dysbalances in the Kyn downstream axis, leading to immunological and neurological consequences. Abbreviations: KynA, kynurenic acid; NAD, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; NK, neutral killer cells; NO, nitric oxide; NOX, NADPH oxidase; Phe, phenylalanine; Arg, arginine; QuinA, quinolinic acid; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Tyr, tyrosine. Metabolites analyzed in this study are in bold and highlighted in orange. Enzymes are shown in blue and amino acids in red text.