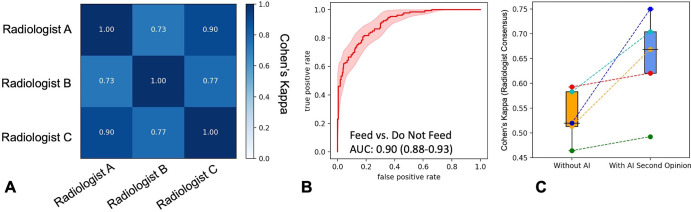
Figure 4:
Effect of nasogastric tube malposition detection model on feed/do not feed decisions of junior physicians. (A) Heatmap shows feed/do not feed interradiologist decision agreement as Cohen κ values. (B) Receiver operating characteristic curve of model performance compared with consensus radiologist feeding decision. Shaded region is 95% CI. (C) Box plots show agreement between junior physicians and consensus radiologist feeding decision without (orange) and with (blue) artificial intelligence (AI) decision support. The box extends from the lower to upper quartile values of the data with a line at the median. The whiskers extend from the box to show the range of the data, bounded by the fifth and 95th data percentile. Points are individual observations and dotted lines are the magnitude of change in κ values for individual clinicians. AUC = area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.