Figure 1.
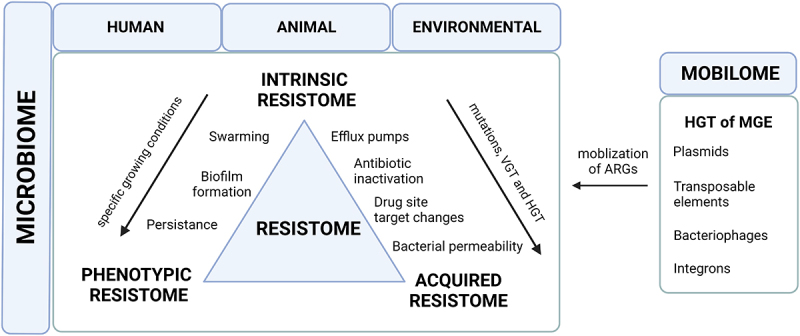
A schematic overview of the human resistome and mobilome. Intrinsic resistance is a property controlled by chromosomes and is related to the general physiology of the microorganism. The acquired resistance is encoded on plasmids and may be classified into four mechanisms: changes in the cell wall that make it less permeable to antibiotics, modifications of enzymes that inactivate antibiotics, changes in the target site of the drug, and efflux pumps that remove antibiotics from the cell. Phenotypic bacterial resistance appears in three categories: persistence, where a subpopulation of bacteria survive even though the majority is inhibited by the antibiotic; formation of biofilms, where bacteria form communities protected by a matrix; and swarming, where cells become hyper-flagellated, allowing them to colonize nutrient-rich environments and become less susceptible to antibiotics. MGE: mobile genetic elements; HGT: horizontal gene transfer; VGT: vertical gene transfer; ARG: antibiotic genetic elements. .
