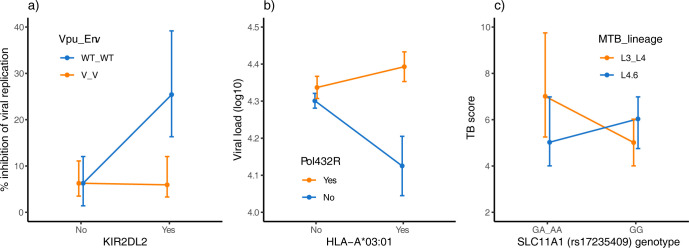
Fig 2. Examples of G×G for continuous traits related to resistance/susceptibility to infectious disease.
(a) G×G between NK cell Killer Immunoglobulin Receptor genotype and HIV genotype for inhibition of viral replication (median ± interquartile range). NK cells with the KIR2DL2 allele strongly inhibit replication of HIV with wild-type alleles at vpu and env (WT_WT) but have limited inhibitory effect on HIV with variant alleles (V_V), while NK cells without KIR2DL2 have limited inhibitory effect on both WT_WT and V_V. Thus, presence/absence of KIR2DL2 affects the range of HIV genotypes an individual is susceptible to, consistent with the GFG scenario. Data extracted from Fig 1B (day 3) of [34]. (b) G×G between HLA-A genotype and HIV genotype for viral load (mean ± SE). Arginine (R) at residue 432 in the pol gene is an immune escape mutation from the HLA-A allele 03:01. In individuals carrying A*03:01, viral load is suppressed in infections with virus without the Pol432R escape mutation, while there is no effect of Pol432 genotype on viral load in individuals without A*03:01 (and no G×G for viral load between Pol432 genotype and other HLA alleles). Thus, there is no indication of a trade-off between resistance to Pol432R and other genotypes as would be the case in an MA type G×G; instead the pattern is consistent with a GFG type G×G. Data from [32]. (c) G×G between SLC11A1 genotype and M. tuberculosis lineage for tuberculosis severity (median ± IQR). A recently evolved M. tuberculosis sublineage (L4.6) in combination with homozygosity for an ancestral SLC11A1 allele (genotype GG) and an original M. tuberculosis lineage (L3 or L4) in combination with ≥1 derived SLCA11A1 allele (genotype GA or AA) is associated with more severe disease than the other combinations of host and pathogen genotypes (the interaction is highly significant: P = 0.00022). Thus, there is a trade-off between resistance to disease by different lineages, consistent with an MA type G×G. Data extracted from Fig 2 in [35]. GFG, gene-for-gene; G×G, host genotype-by-pathogen genotype interaction; MA, matching allele.