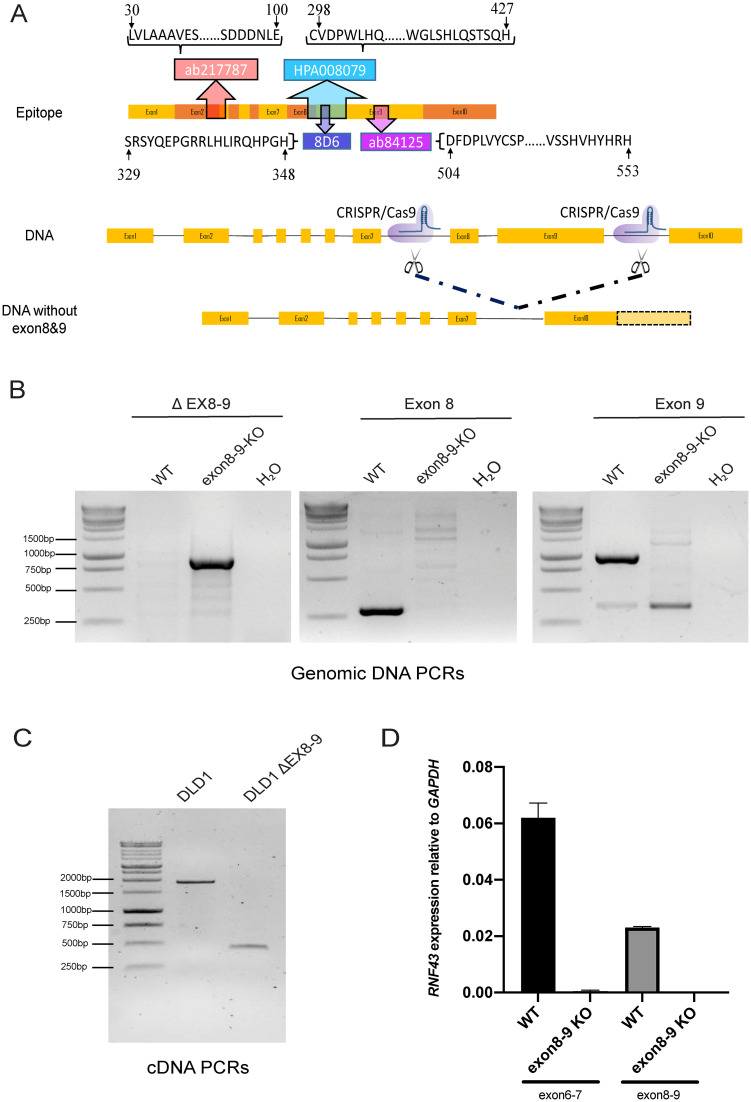
Fig 1. Epitope location and generation of DLD-1 RNF43 ΔEX8-9 clone.
A. Schematic representation of RNF43 mRNA and epitope location of RNF43 antibodies. The ab217787 antibody was raised against a N-terminal epitope encoded by exons 2 and 3, while the other three antibodies were raised against epitopes encoded by exons 8 and 9. A DLD-1 cell clone was generated that entirely misses these exons leading to a p.(Glu284_Pro769delext*56) deletion on protein level. B. Confirmation of correct deletion of exons 8 and 9 on DNA level. Left panel shows PCR with primers flanking the deletion. The expected approximate 900bp fragment is observed in the ΔEX8-9 clone, while the original 4kb fragment is too big to be amplified. Middle and right panels show, respectively, PCRs for exons 8 and 9, leading to the expected 283 and 914bp fragments in the wild-type cell line, whereas only non-specific bands are observed in the ΔEX8-9 clone. DNA marker used is the 1kb DNA ladder from Promega (#G5711) C. Confirmation of correct deletion of exons 8 and 9 on mRNA level. Primers flanking exons 8 and 9 reveal the expected 1904 and 445bp fragments, respectively, for the wild-type cells and ΔEX8-9 clone. D. A quantitative RT-PCR analysis of RNF43 exons 8–9 shows undetectable levels in the ΔEX8-9 clone. Interestingly, as shown by a qRT-PCR for exons 6–7, total RNF43 levels are decreased about 200-fold in this clone. In conclusion, we have successfully generated a DLD-1 clone that shows strongly reduced levels of RNF43 mRNA entirely lacking exons 8 and 9.