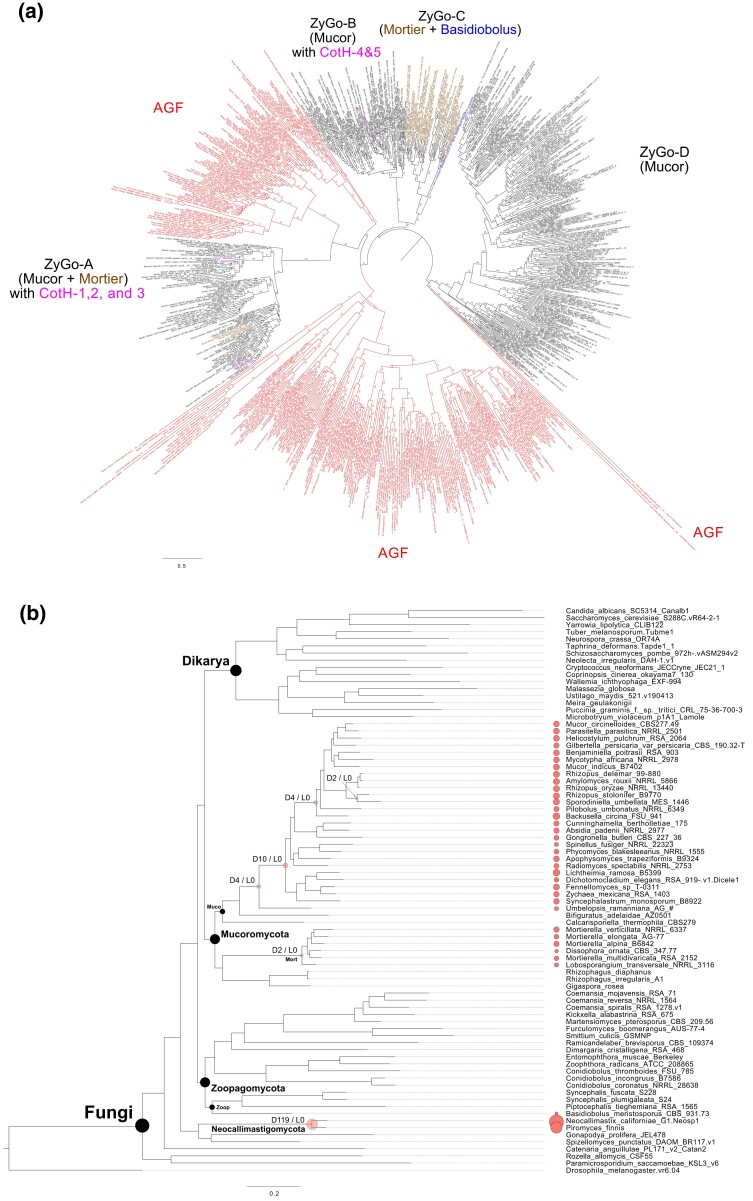
Fig. 6.
Phylogenetic analysis and evolution of CotH in Kingdom Fungi. (a) The 754 fungal CotH copies were identified from Mortierellomycotina (brown), Mucoromycotina (black), Basidiobolus (blue), and Neocallimastigomycota (red). The CotH phylogenetic tree was midpoint rooted and reconstructed using the maximum likelihood method with bootstrap supports (out of 100) labeled on each branch. The analysis included previously classified CotH families 1–5 (pink) to help categorize newly identified fungal CotH. (b) Reconstruction of CotH evolution in Kingdom Fungi with Notung. CotH copies identified in each genome were plotted at tree tips with proportional sizes. Nodes with more than one duplication event were highlighted with red bubbles and labeled with duplication (“D”) and loss (“L”) events. Node abbreviation: Muco, Mucoromycotina; Mort, Mortierellomycotina; Zoop, Zoopagomycotina.