Fig. 4.
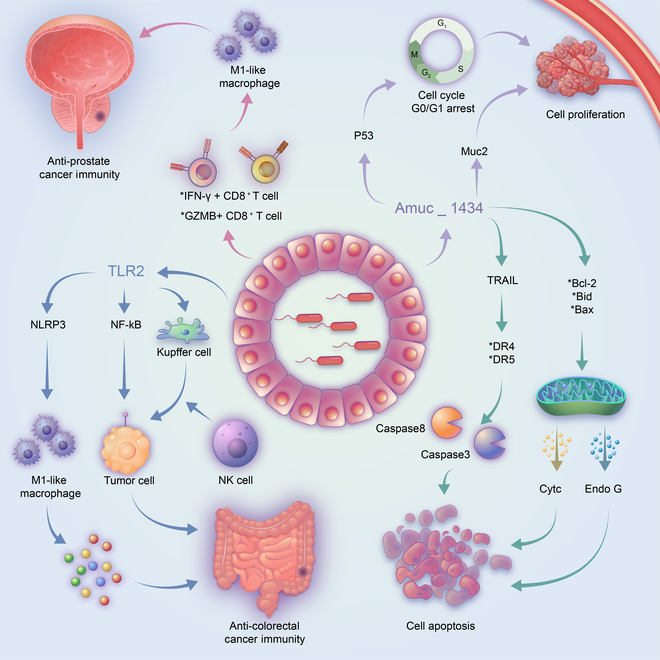
The regulatory role of A. muciniphila in neoplastic disease. Amuc_1434 induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest by promoting p53 expression in colorectal cancer. Amuc_1434 inhibits the proliferation of LS174T cells through regulation of Muc2. Amuc_1434 activates death receptors and mitochondrial apoptosis pathways to promote apoptosis in LS174T cells. In colorectal cancer, A. muciniphila induces M1-like macrophage polarization by regulating the TLR2/NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways; activated NLRP3 in Kupffer cells promotes the recruitment of NK cells to kill tumor cells. A. muciniphila extracellular vesicles enhance the anti-prostate cancer immune response of cytotoxic T lymphocytes by increasing the proportion of GZMB+CD8+ T cells and IFNγ+CD8+ T cells.
