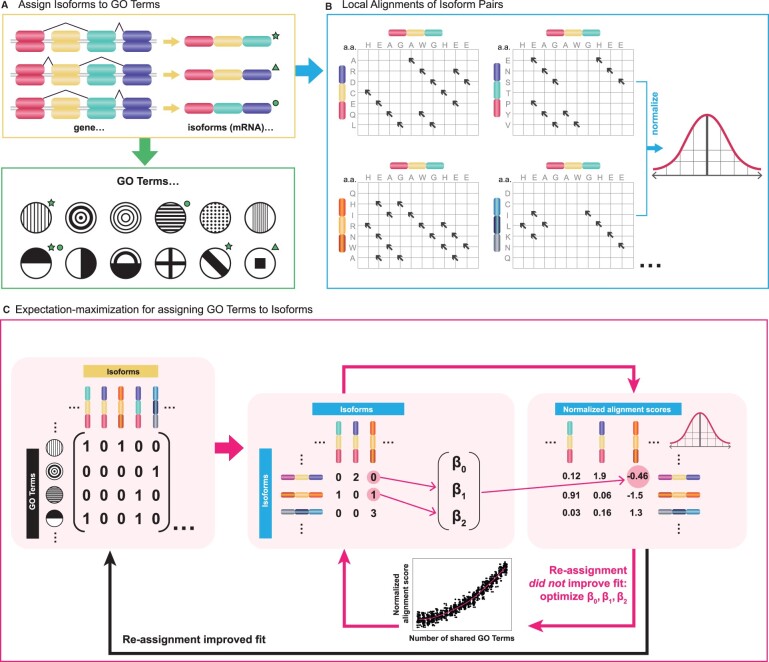
Figure 1.
Optimization algorithm for assigning functions from genes to isoforms. (A) The initialization of isoform functions, i.e. the initial isoform-to-GO-terms assignment, is performed by assigning isoforms GO terms that are associated with their predicted InterPro domains. (B) Local alignment scores are computed between every pair of isoforms, and the scores are log transformed and standardized. (C) The isoform-to-GO-term binary matrix is multiplied by its transpose to obtain a matrix of the number of shared GO terms between each pair of isoforms. These values are then used as the independent variable in a quadratic model with parameters to predict the normalized local alignment scores between pairs of isoforms. The GO-term assignment is optimized by a stepwise procedure that uses a GA (Section 2) until no further improvement in the model fit is possible (black arrow at bottom), at which point the GO-term assignment is fixed and new parameter values are obtained by optimizing the fit of the model (pink arrow at upper right). These two steps of GO-term assignment optimization and parameter values optimization are repeated consecutively until no further improvement can be obtained