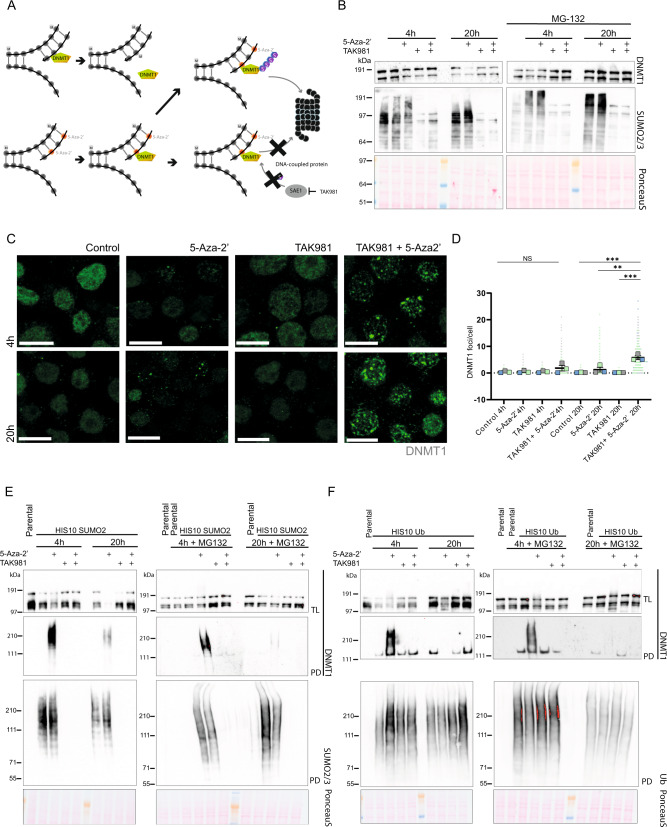
Fig. 1. SUMOylation inhibition rescues DNMT1 degradation upon 5-Aza-2’ treatment and contributes to prolonged presence of DNMT1 in foci.
A Mechanistic model for combining the drugs 5-Aza-2’ and TAK981. 5-Aza-2’ incorporates into the DNA at the site of cytidine. DNMT1 binding to 5-Aza-2’ gets trapped and is subsequently massively SUMOylated, ubiquitinated and degraded by the proteasome. Upon 5-Aza-2’and TAK981 treatment, DNMT1 remains entrapped at the DNA. B Namalwa cells were cultured in suspension and treated for 4 or 20 h with 1 µM 5-Aza-2’ and/or 1 µM TAK981 or DMSO 0.1% as control with or without MG132 10 µM for 4 h and 2.5 µM for 20 h. Total lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibodies directed against DNMT1 and SUMO2/3. PonceauS staining was used as control. C DNMT1 foci were visualized by confocal microscopy. Namalwa cells were treated for 4 or 20 h with 1 µM 5-Aza-2’ and/or 1 µM TAK981 or DMSO 0.1% as control and cells were spun onto glass coverslips and stained. Representative images are depicted. Scale bars represent 10 µm. D Quantification of images from C. The graph depicts DNMT1 foci. Dots represent the numbers of DNMT1 foci/cell. 100 cells per replicate were analyzed (n = 3). P-value ** ≤ 0.01, *** ≤ 0.005. One-way ANOVA was performed with Graphpad Version 9.3.1. E, F Respectively show Ni-NTA pulldown of His10-SUMO2- and His10-ubiquitin. Namalwa cells were cultured in suspension and treated for 4 or 20 h with 1 µM 5-Aza-2’ and/or 1 µM TAK981 or DMSO 0.1% as control with or without MG132 10 µM for 4 h and 2.5 µM for 20 h. Total lysates (TL) and elutions from His10 pulldowns (PD) were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies directed against DNMT1, SUMO2/3 or ubiquitin. Equal loading was verified with Ponceau S staining.