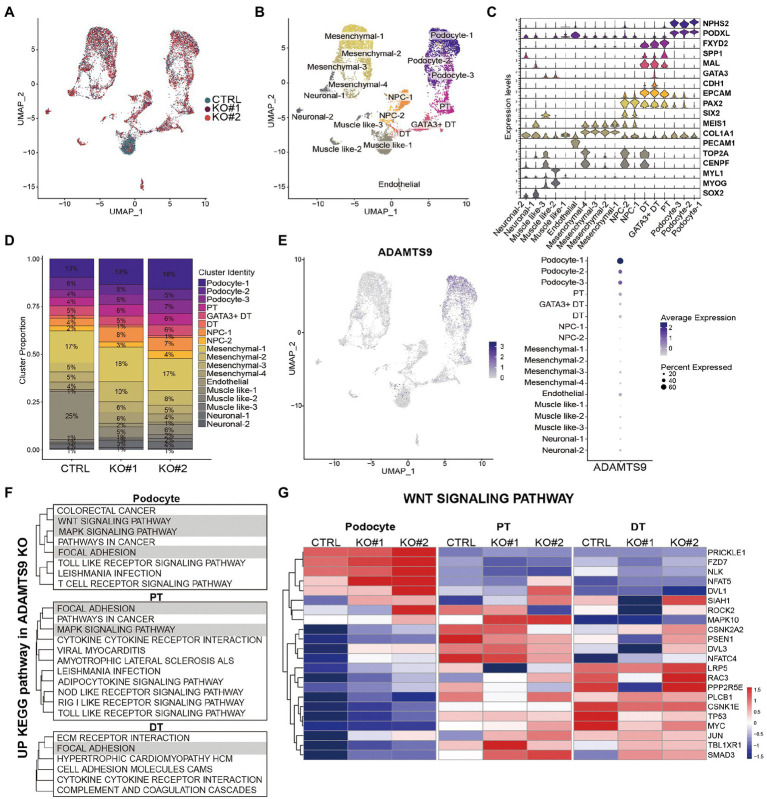
Figure 3.
scRNA-seq analysis of the control and ADAMTS9 knockout kidney organoids. (A) UMAP visualization of single-cell transcriptomic profiles from two ADAMTS9 knockout organoids and a control organoid. (B) UMAP plots showing 18 clusters identified by canonical marker genes. (C) Proportion of clusters across control and ADAMTS9 knockout organoids with corresponding percentages. (D) Violin plots showing the expression of canonical and data-derived kidney markers used to identify nephron clusters in D29 organoids: podocytes (NPHS2, PODXL), proximal tubules (FXYD2, SPP1), distal tubules (MAL, CDH1), immature distal nephrons (GATA3 + DT), and nephron progenitor cells (PAX2, SIX2). Mesenchymal, endothelial, and off-target cells were also identified. (E) ADAMTS9 expression across all clusters in control organoids. (F) Analysis of leading edge genes from GSEA of differentially expressed genes in podocytes, PT, and DT clusters showed three enriched pathways: focal adhesion, MAPK pathway, and Wnt pathway. (G) Heatmap showing expression of Wnt signaling pathway-related genes identified by GSEA in podocytes, PT, and DT clusters in control versus ADAMTS9 knockout kidney organoids.