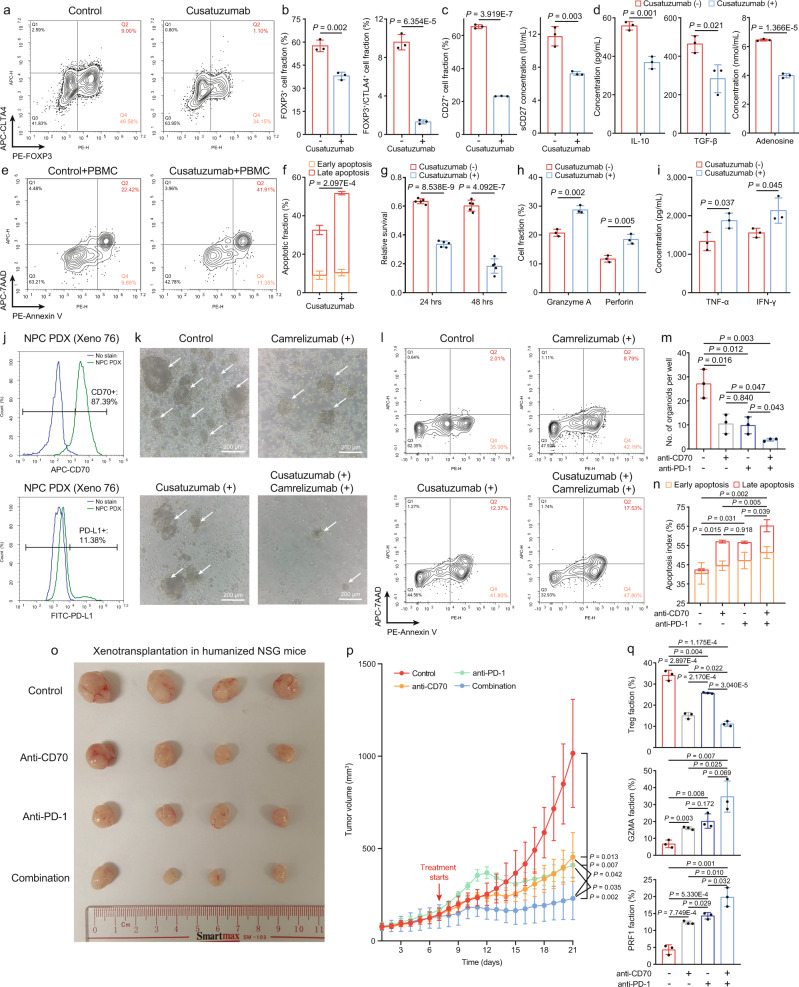
Fig. 4. Therapeutic inhibition of CD70 promotes anti-tumor immunity and anti-PD-1 efficacy.
a, b Immunophenotyping of CD4+ naïve T cells treated with IgG antibody and cusatuzumab (n = 3, two-sided unpaired t test). c The change of surface and sCD27 in the co-cultured systems treated with IgG antibody and cusatuzumab (n = 3, two-sided unpaired t test). d The change of immunosuppressive factors in the co-cultured systems treated with IgG antibody and cusatuzumab (n = 3, two-sided unpaired t test). T-cell cytotoxicity measured in the IgG-treated and cusatuzumab-treated (e and f, flow cytometry, n = 3; g, XTT assay, n = 5) C666/PBMC co-culture systems (two-sided unpaired t test). The change of CD8 + T-cell cytotoxicity markers (h, flow cytometry) and cytokines (i, ELISA) in IgG-treated and cusatuzumab-treated C666/PBMC co-culture systems (n = 3, two-sided unpaired t test). j Expression of CD70 and PD-L1 in NPC PDX Xeno76. T-cell cytotoxicity measured in the IgG-treated and cusatuzumab-treated (k and m, microscopy; l and n, flow cytometry) PDX/PBMC co-culture systems (n = 3, two-sided unpaired t test). o, p Tumor growth in PDX-bearing humanized mice treated with different regimens (n = 4 for each treatment group), measured from day 1 post intravenous PBMC injection (two-sided unpaired t test). q The change of Tregs and cytotoxic T cells in tumors compared between every two treatment groups (n = 3 per treatment group, two-sided unpaired t test). The n number represents n biologically independent samples/experiments in each group. The data are presented as the mean ± SD (bar plots).