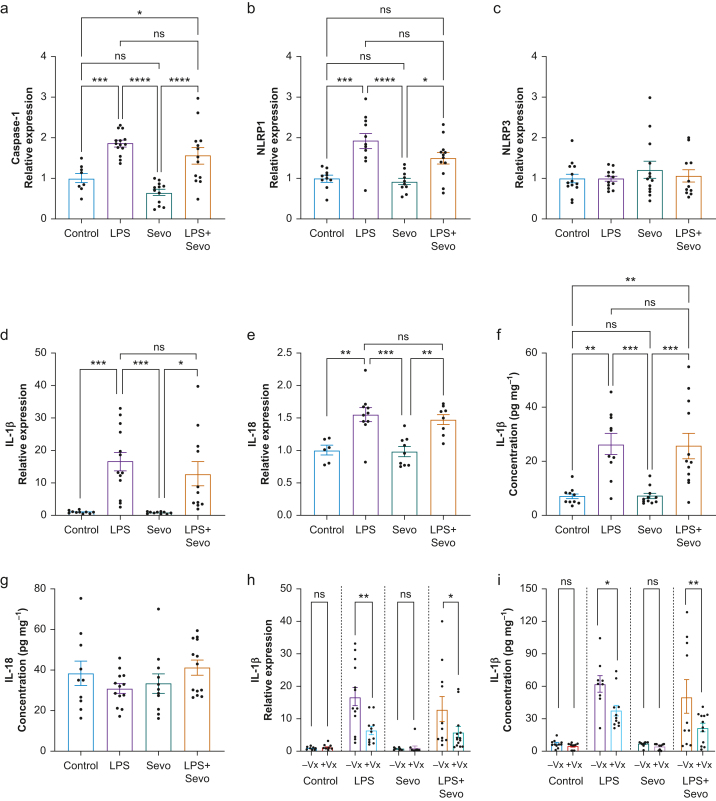
Fig 4.
Quantification of inflammasome signalling after treatment with LPS, sevoflurane, or both. (a) LPS alone or in combination with sevoflurane induced higher levels of caspase-1 mRNA compared with control or sevoflurane. Caspase-1 mRNA did not differ between LPS alone or LPS+sevoflurane, indicating that caspase-1 induction is primarily LPS-driven. (b) Hippocampal NLRP1 mRNA followed a similar pattern of induction, although LPS+sevoflurane was marginally insignificant compared with control (P=0.063). (c) Conversely, we observed no differences in NLRP3 mRNA across treatments. Analysis of IL-1β and IL-18 mRNA (d, e) and protein (f, g) levels in hippocampus revealed that upregulation of these cytokines was primarily LPS-driven, whereas sevoflurane did not differ from the control. Whereas mRNA was upregulated after LPS treatment, IL-18 protein levels were not different at this time point. (h, i) Pretreatment with Vx-765 (+Vx), a selective caspase-1 inhibitor, reduced IL-1β mRNA (h) and protein (i) levels. Vx-765 had no effect on baseline IL-1β levels, nor in the sevoflurane group. In each pair, 10% DMSO was administered as vehicle control (–Vx). (a–g) One-way anova+Tukey's post hoc; (h, i) two-way anova+Sidak's post hoc. ∗P<0.05, ∗∗P<0.01, ∗∗∗P<0.001, ∗∗∗∗P<0.0001. anova, analysis of variance; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; IL, interleukin; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NLRP1, NLR family pyrin domain containing 1; Sevo, sevoflurane.