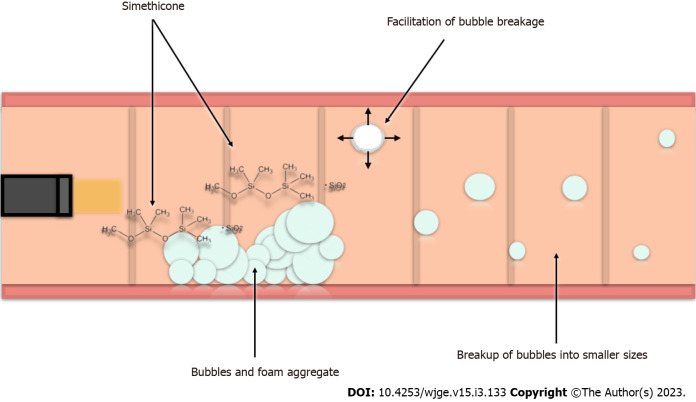
Figure 1.
Functioning of simethicone at the level of the intestinal mucosa. Simethicone is a surfactant causing a reduction in the surface tension of intestinal bubbles. This reduction results in the aggregate of bubbles adhering to the colic mucosa being weaker with the facilitation of bubble reduction. As a result, larger bubbles are divided into smaller bubbles that have a greater ease of intestinal transit. The silicon dioxide component of dimethicone has an additional role, with an extensive molecular surface area that can promote bubble rupture. The breakdown of foam and bubbles and formed gas can be either absorbed by the intestinal wall or eliminated by intestinal transit. This likely explains the ameliorative effect on patients' symptoms.