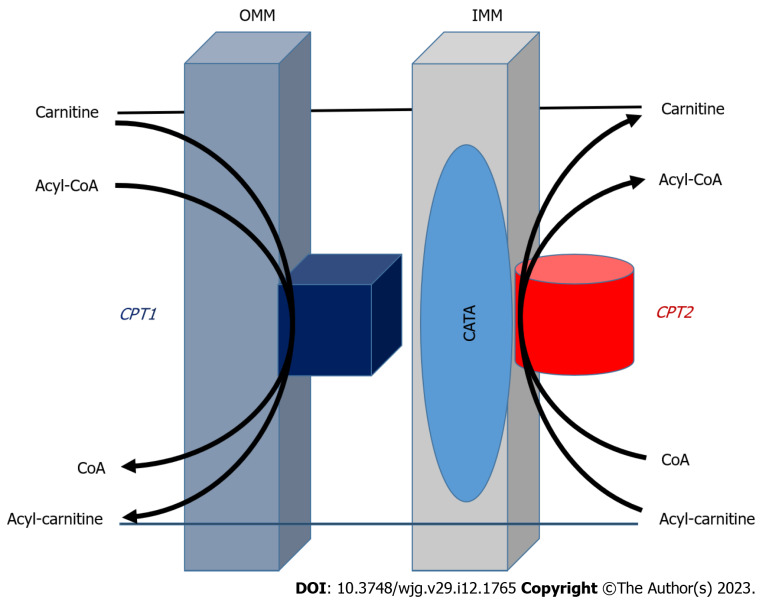
Figure 1.
Transport system of fatty acid oxidation in outer mitochondrial membrane and inner mitochondrial membrane[11,65]. Fatty acid β-oxidation is catalyzed by enzymes located in outer and inner mitochondrial membrane to form acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) in the participation with ATP and CoA. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase (CPT)-I promotes the conversion of acyl-CoA to acyl-carnitine that is transported to mitochondrial interior with the help of translocase on the intima of mitochondria. Under the catalysis of CPT-II, acylcarnitine releases carnitine, and then converted to acyl-CoA to enter β-oxidation. The CPT system with carnitine acyl-carnitine translocase play a vital part in the transport system for esterification of fatty acids through the mitochondrial membrane and CPT-II as a key rate-limiting enzyme for fatty acid β-oxidation. OMM: Outer mitochondrial membrane; IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane; CACT: Carnitine acyl-carnitine translocase; CPT: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase; CoA: Coenzyme A.