Fig. 3.
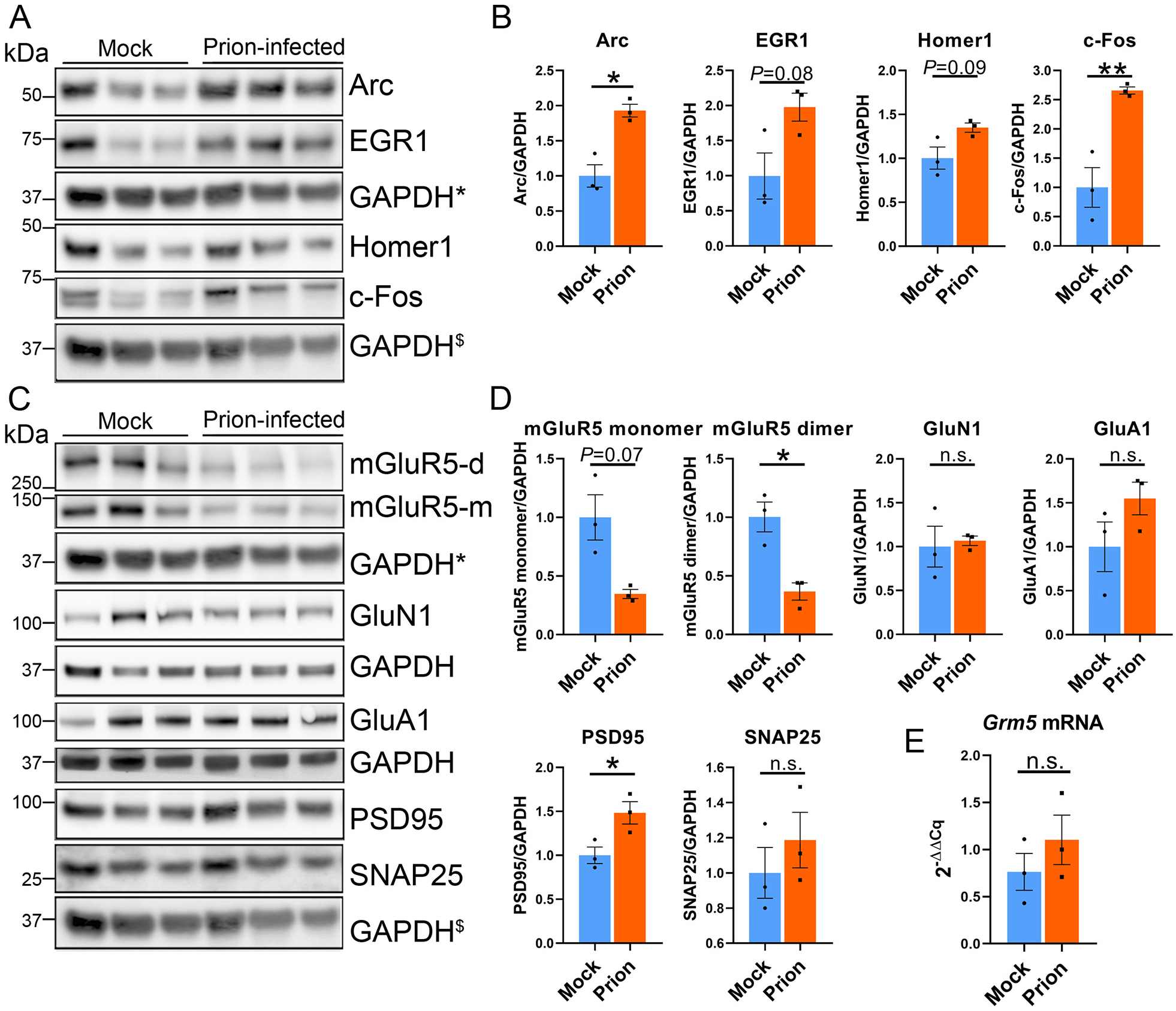
Increased Arc protein correlates with a decrease in mGluR5, but not GluN1 or GluA1. (A, B) Immunoblots and quantification of hippocampal proteins show increases in Arc and c-Fos at the 40% timepoint post-prion exposure. (C, D) Immunoblots and quantification of synapse-associated proteins, including receptors (mGluR5, GluN1, and GluA1), a presynaptic protein (SNAP25), and a postsynaptic protein (PSD-95) reveal a decrease in mGluR5 dimers, and a modest increase in PSD-95. (E) qRT-PCR reveals no change in Grm5 transcripts. * and $ indicate the same GAPDH loading controls for proteins immunoblotted on the same membrane. n = 3 male mice per group. Welch’s t-test, *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01.
