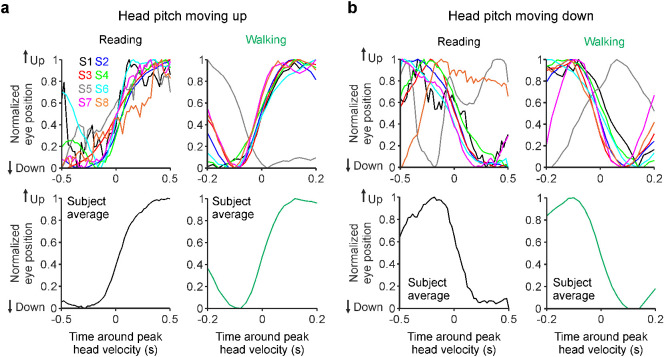
Figure 8.
Head-triggered eye movements are slower during reading than walking. (a) Normalized eye position centered at the point of maximum head velocity for reading (top left) and walking (top right), shown for each individual subject (top) and the subject average (bottom). The scale in the x-axis is two times larger for reading than walking because the head-triggered eye movements were two times slower. (b) Same as a, for head pitch moving down. The time course was similar across most subjects but slower than the average for one subject with corrected myopia (S5, gray lines) and a subject with amblyopia (S8, orange line).