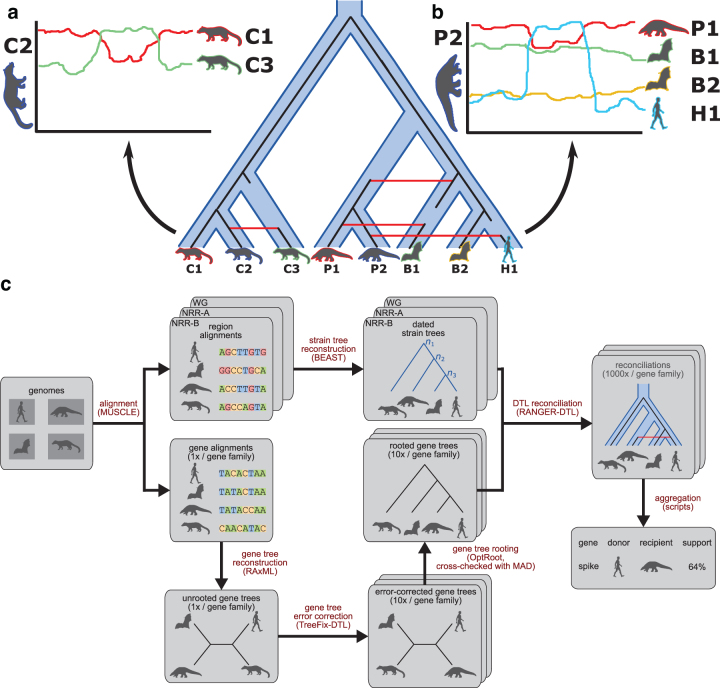
FIG. 1.
virDTL enables inference of ancestral recombination. The figure shows a cartoon example of the virDTL pipeline applied to a toy dataset containing viruses from three civet cats, two pangolins, two bats, and one human. (a) Commonly used tools such as Simplot and RDP are well-suited to inferring recent recombinations between strains of interest, where the recombination signal is clear in the sequence similarity profile. (b) However, in cases where recombination has occurred between ancestral strains, and multiple recombinations have occurred in a single lineage, it becomes significantly more difficult to disentangle the sequence similarity signal to infer all recombinations. (c) Our model-based computational protocol, virDTL, takes into account the entire evolutionary history of a gene family, including several sources of inference uncertainty. A credible strain tree is estimated using nonrecombinant regions of the genome, and multiple gene tree candidates are inferred and error-corrected and reconciled against the strain tree to infer HGTs. In addition to accounting for gene tree topological and rooting uncertainty, we reconcile the same gene tree and species tree multiple times to capture the full landscape of uncertainty in inferring recombination.