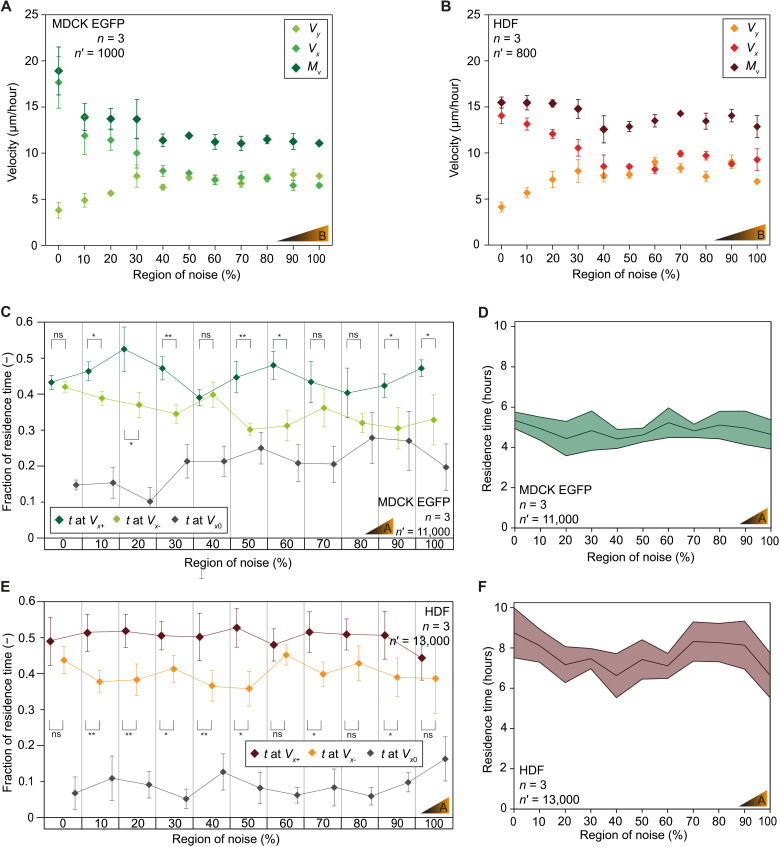
Fig. 3. Topographic noise controls directional migration and modulates contact guidance.
(A and B) Velocity of directional migration in isolated MDCK cells or HDF adhering to experimental substrates presenting a low gradient of topographic noise (substrate B; table S1). (C and D) Migration persistence and total residence time for isolated MDCK cells in the direction of increasing (t at Vx+) or decreasing topographic noise (t at Vx−) or without migration (t at Vx0). (E and F) Migration persistence and total residence time for isolated HDF on individual regions of topographic noise. n = number of independent experiments, n′ = number of analyzed cells. Error bars correspond to the measured standard error of the mean. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01; ns, not significant, by Mann-Whitney test and two-sample t test.