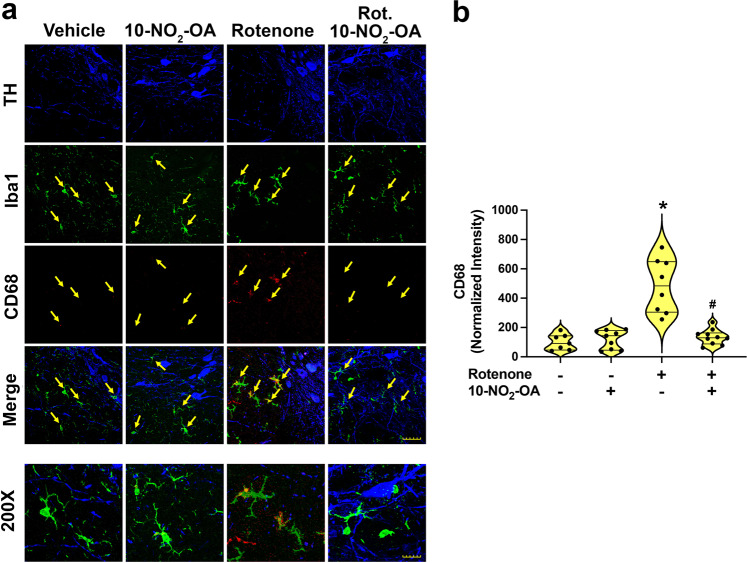
Fig. 6. 10-NO2-OA inhibits rotenone-induced microglial activation in SNpc (Cohort 2).
a Rats treated with rotenone showed a significant increase in microglial activation (green) in SNpc analyzed immunohistochemically for the microglial activation marker, CD68 (red). Co-administration of 10-NO2-OA (45 mg/Kg) inhibited rotenone-induced microglial activation (Scale bar main figure: 35 μm; Scale bar ×200 magnification: 15 μm). b Quantification of the signal relative to CD68 in microglia (Iba1) with symbols that represent the normalized means of the intensity (with Vehicle set at 100%) from a single rat (4 slices/brain). The number of animals per treatment group were the following: Vehicle (n = 7), 10-NO2-OA (n = 9), Rotenone (n = 8), Rotenone + 10-NO2-OA (n = 10). Statistical analysis was performed by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni correction (*p < 0.0001 compared to Vehicle and 10-NO2-OA, #p < 0.0001 compared to Rotenone).