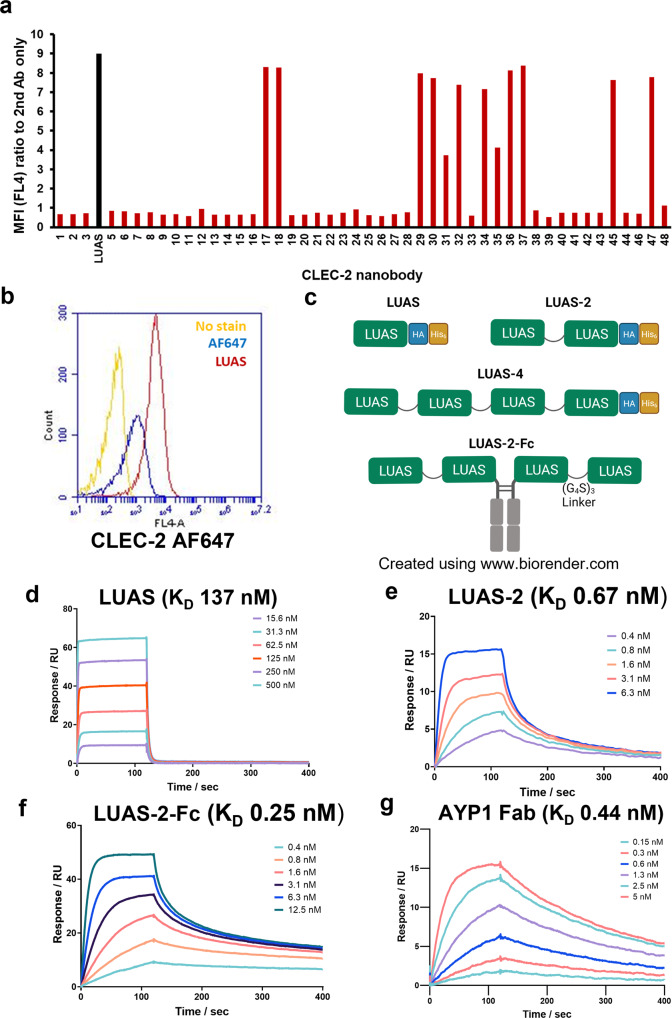
Fig. 1. Characterisation of CLEC-2 ligands.
a Representative flow cytometry data showing binding of CLEC-2 nanobodies (7 nM) to human platelets measured with Alexa Fluor-647 anti-His tag antibody secondary staining (5 μg/ml) to the his-tag on the nanobodies. Data presented as MFI normalised for MFI of secondary staining alone (a.u.). The strongest binder nanobody LUAS (Black bar) is highlighted (n = 3 biologically independent experiments). b Representative fluorescence intensity histogram overlays showing binding of LUAS (red) (7 nM) to platelets measured with anti-Alexa Fluor-647 (AF647) anti-His tag antibody secondary staining (5 μg/ml) to the his-tag on the nanobodies. Yellow histogram shows platelets with no stain and blue histogram shows secondary staining alone. c Schematic representation of the CLEC-2 monovalent, LUAS, divalent LUAS-2 and tetravalent LUAS-4 and LUAS-2-Fc nanobody ligands. LUAS subunits are connected with (G4S)3 amino acid linkers and have HA and His6 tags. The tetravalent LUAS-2-Fc was made by dimerisation of divalent LUAS-2 with a mouse Fc domain (IgG2a). d–g Representative SPR sensograms showing the binding of LUAS, LUAS-2, LUAS-2-Fc and AYP1 Fab to an immobilised surface of recombinant His6-tagged CLEC-2 (residues 55-229). The binding affinities, KD, were determined as 137 ± 7, 0.67 ± 0.09, 0.25 ± 0.09 and 0.44 ± 0.03 nM for LUAS, LUAS-2, LUAS-2-Fc and AYP1 Fab, respectively. Values were calculated by kinetic analysis using a global fitting model within the Biacore T200 evaluation software (n = 3 biologically independent experiments).