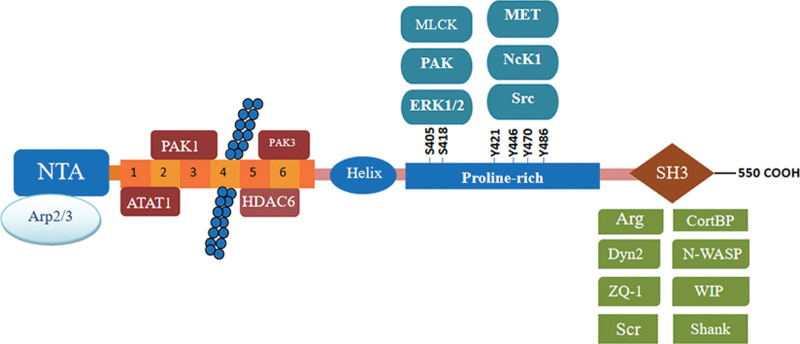
Figure 2.
① Cortactin’s NTA binds to and activates the Arp2/3 complex, which regulates branching actin assembly as well as F-actin polymerization and contraction. ② The 6.5 F-actin repeat domain: The fourth in the repeat sequence is responsible for binding to F-actin (F-actin). Post-translational modifications of the 6.5 F-actin repeat domain can regulate the function of cortactin, and these modifications include phosphorylation and acetylation of PAK1, PAK3, ATAT1, and HDAC6. ③ An α-helix and a proline-rich region: Multiple tyrosine phosphorylation sites, such as Y421, Y446, Y470, Y486, etc., are found in these areas, which are phosphorylated by kinases such as Src, Fer, c-Met, and NCK1. ERK, PAK, MLCK, and other kinases phosphorylate two serine phosphorylation sites, S405 and S418, respectively. ④ SH3: Many cytoskeletal, membrane transport, and signaling proteins, such as N-WASP, ZO-1, CortB, and Dynamin2, bind to the C-terminal SH3 structural domain. Arp2/3 = actin-related protein 2/3, N-WASP = neural-WASP famly verprolin-homologous protein family.