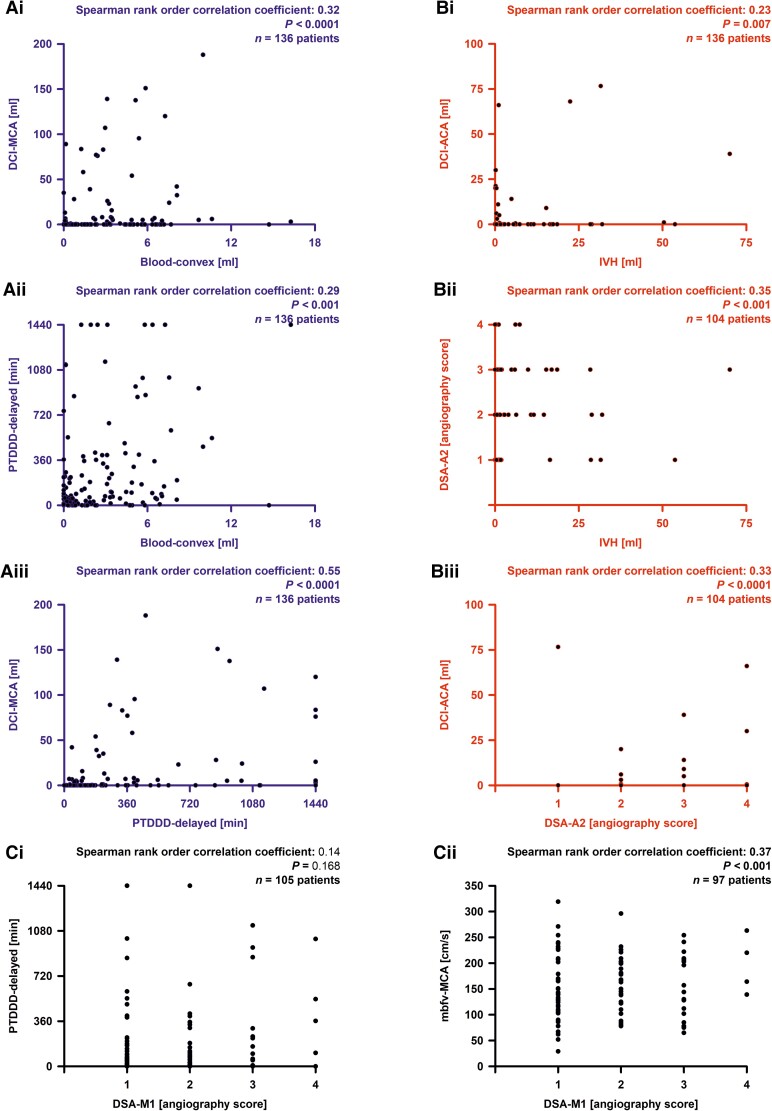
Figure 4.
Correlation analyses. In the principal component and path analyses, we found two paths, one from extravascular blood volume component (bloodcomponent) to delayed cerebral ischaemia component (DCIcomponent) with spreading depolarization component (SDcomponent) as mediator variable, and one from IVH to DCIcomponent with DSA component as mediator variable. (A) Three strongest correlations between individual variables from the three variable groups involved in the path from bloodcomponent to SDcomponent to DCIcomponent. (B) Three strongest correlations between individual variables from the three variable groups involved in the path from IVH to DSAcomponent to DCIcomponent. (Ci) The electrode strip was typically located on the cortex of the territory of the MCA. However, there was no correlation between angiographic vasospasm in the M1 segment (or M2 segment, see Supplementary Table 1) of the MCA (DSAM1) with the SD variables [shown here is the PTDDDdelayed (peak value of a recording day for the total (cumulative) SD-induced depression durations during the delayed period)]. (Cii) In contrast, the TCD-determined peak mean blood flow velocity of the MCA (mbfvMCA) correlated with DSAM1. bloodconvex = subarachnoid blood volume on the cerebral convexity; DCIACA = delayed infarct volume in the territory of the anterior cerebral artery (ACA); DCIMCA = delayed infarct volume in the territory of the MCA; DSAA2 = DSA score of the A2 segment of the ACA.