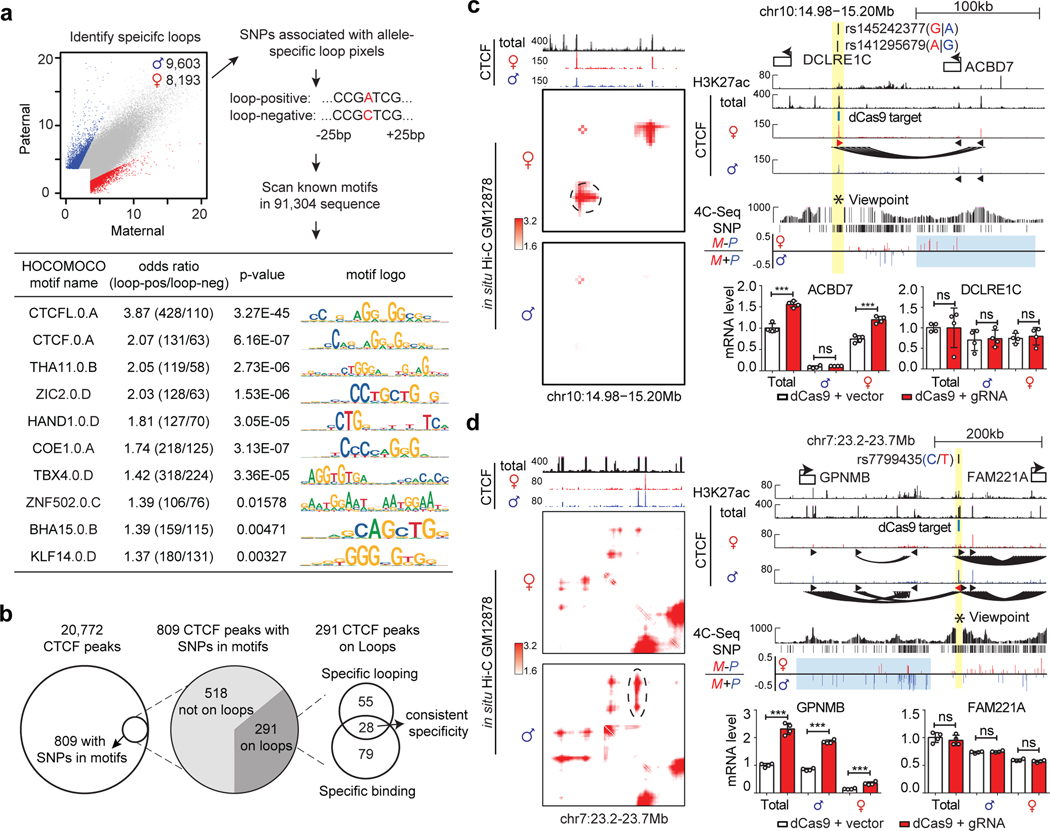
Figure 8. Allelic DeepLoop maps can pinpoint common SNPs that affect chromatin loops.
a, Flowchart showing the de novo motif findings associated with allele-specific chromatin loops. The scatterplot highlights the allele-specific loops. The 51-base sequences (25bp up/down) around the SNPs are used to scan for motifs significantly enriched in the loop-positive alleles. Fisher’s exact test was performed to measure the motif enrichment. b, Summary of the procedure to identify causal SNPs for allele specific CTCF loops and TF occupancy. c-d, Using “insulator epigenome editing” to validate the transcription regulatory functions of two selected allelic-specific CTCF loops. Both contact heatmaps and genome browser tracks are included to show the locations of SNPs, the specific CTCF peaks and DNA loops. 4C-seq tracks shows the chromatin interactions with the SNP region as viewpoint (highlighted in yellow). Tracks of allelic 4C-seq analysis show the maternal (red) or paternal (blue) preference of 4C-seq signal. The regions of interest are highlighted in light blue. The bar plots show the changes of nearby gene expression with allele-specific RT-qPCR upon CTCF-blocking with dCas9. N=2 biologically independent experiments. All data are presented as means ± SEM from 4 replicated experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. NS, no significant difference. Two-sided Wilcoxon test. (More results in Extended Data Figure 10).