Figure 4.
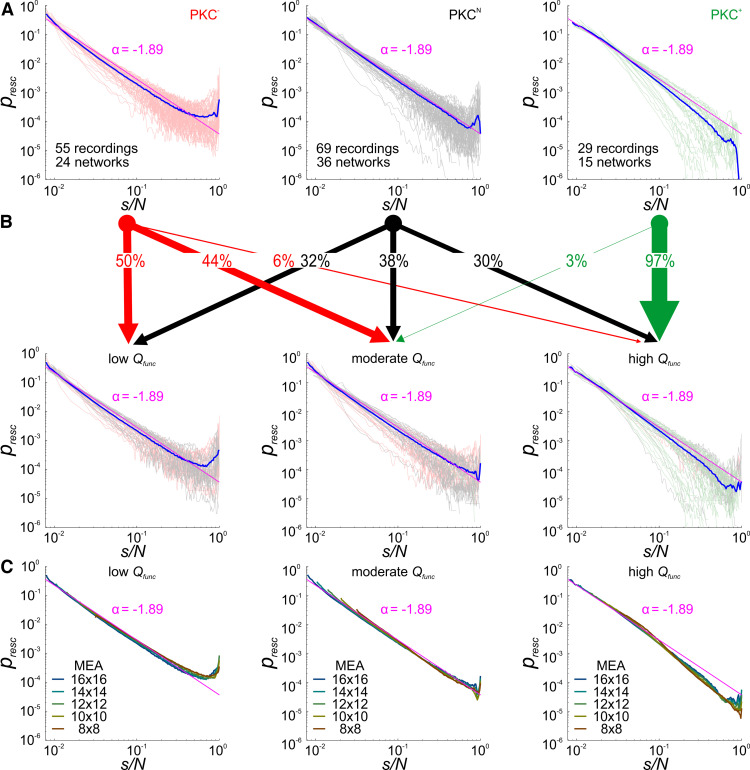
Moderate functional modularity promotes close to power law ASDs. A, ASDs from the respective PKC conditions with avalanche size s normalized by the number of recordings sites N using α = −1.89 (obtained for close to power law ASDs, Fig. 2H) for rescaling to a common axis. Individual networks were typically recorded twice in the course of development after 18 DIV. B, Networks were assigned into the three categories representing low (<33.3rd percentile), moderate, and high (>66.7th percentile) Qfunc. PKC− networks were mostly part of the low Qfunc group with convex ASDs, whereas PKC+ networks dominated in the high Qfunc group with concave ASDs. PKCN networks contributed most to the moderate Qfunc group with ASDs close to a power law but also constituted large fractions in the other groups. ASD line color refers to PKC conditions in A. Blue lines show the respective Qfunc group averages. C, Reducing the virtual MEA size by successively removing perimeter electrodes did not fundamentally change ASDs.