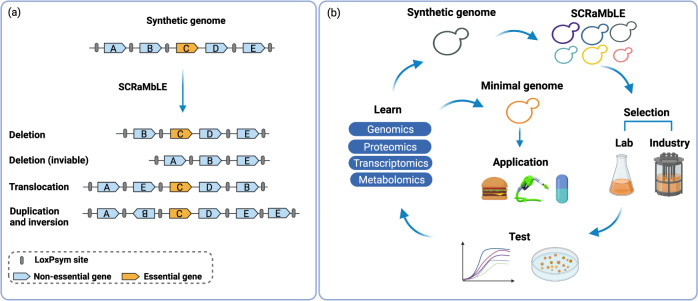
Fig. 4. Genome minimisation by SCRaMbLE.
a Genome diversity generated by SCRaMbLE. LoxPsym sites are inserted in the 3’UTR of all non-essential genes. Upon induction of SCRaMbLE, various genome rearrangement events can happen, for example, deletion of non-essential gene ‘A’, translocation of ‘E’ and ‘B’, inversion of ‘B’ and duplication of ‘E’. However, deletion of a gene-cassette containing essential gene ‘C’ leads to cell death. b Creation of minimal and industrial-minimal genomes via SCRaMbLE. Genome rearrangements including deletions of large segments can occur upon activation of SCRaMbLE. Applied with appropriate selection pressures, the SCRaMbLEd cells with reduced genome size can be selected under lab conditions, and under industrial conditions in parallel, such as different carbon source utilisation, stress conditions, and etc. The selected strains are then tested for phenotypes and analysed by ‘omics’ approaches, which would shed light on future rational design of minimal genomes. Iterative rounds of SCRaMbLE-Selection-Test-Learn can be applied before the generation of minimal genomes or industrial minimal genomes, which can serve as a simplified chassis for industrial engineering.