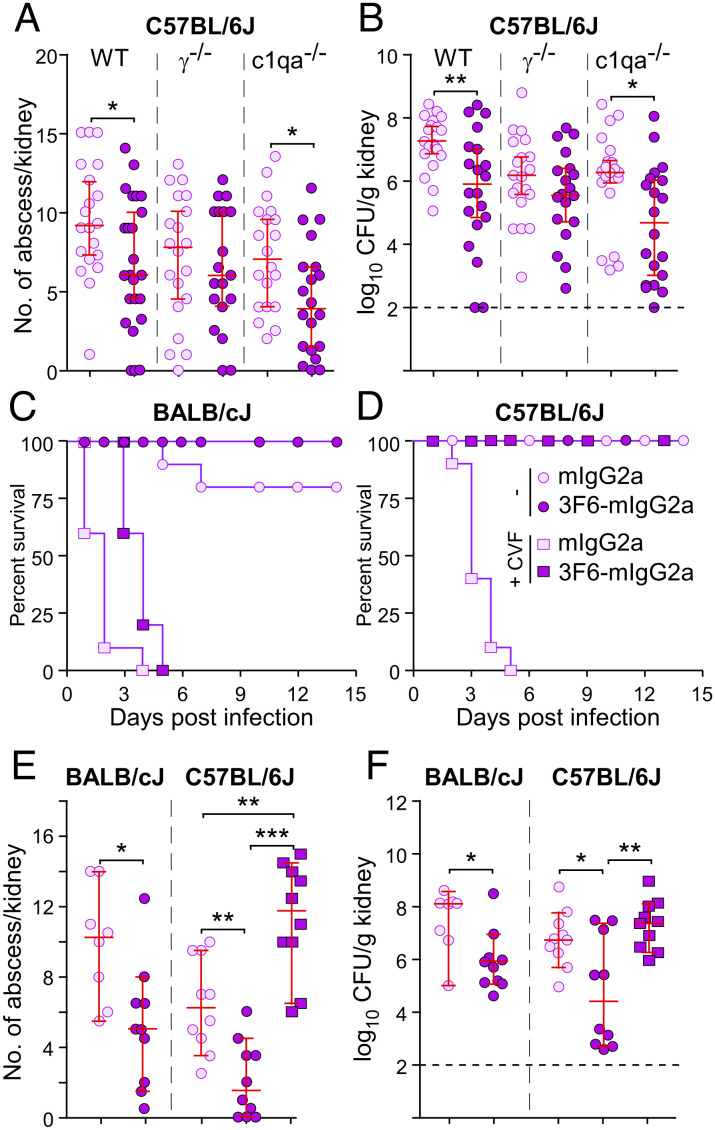
Fig. 3.
3F6-mIgG2a protects BALB/cJ and C57BL/6J mice via distinct mechanisms. (A and B) Passive immunization with 3F6-mIgG2a protects C57BL/6J WT and c1qa−/− mice but not γ−/− mice against S. aureus MW2 infection. mIgG2a or 3F6-mIgG2a (10 mg/kg) was given before challenge with MW2. Fifteen days post infection, kidneys (n = 20 animals, from two independent experiments) were removed to enumerate surface abscesses (A) and CFU (B). (C–F) 3F6-mIgG2a requires complement to protect BALB/cJ but not C57BL/6J mice against S. aureus infection. Test antibodies (10 mg/kg body weight) with or without CVF (150 μg/kg body weight) were administered to BALB/cJ (n = 7 to 10 from two independent experiments) and C57BL/6J (n = 8 to 10 from two independent experiments) mice before challenge with S. aureus MW2. Survival (C and D) was recorded daily, and surface abscesses (E) and bacterial loads (F) in kidneys were enumerated 15 d post infection. Data are presented as medians ± 95% CI (A, B, E, and F). Dashed lines (B and F) indicate the lower limit of detection. Significant differences were identified with the two-tailed Mann–Whitney test (A and B) or one-way ANOVA with Kruskal–Wallis test (E and F; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05).