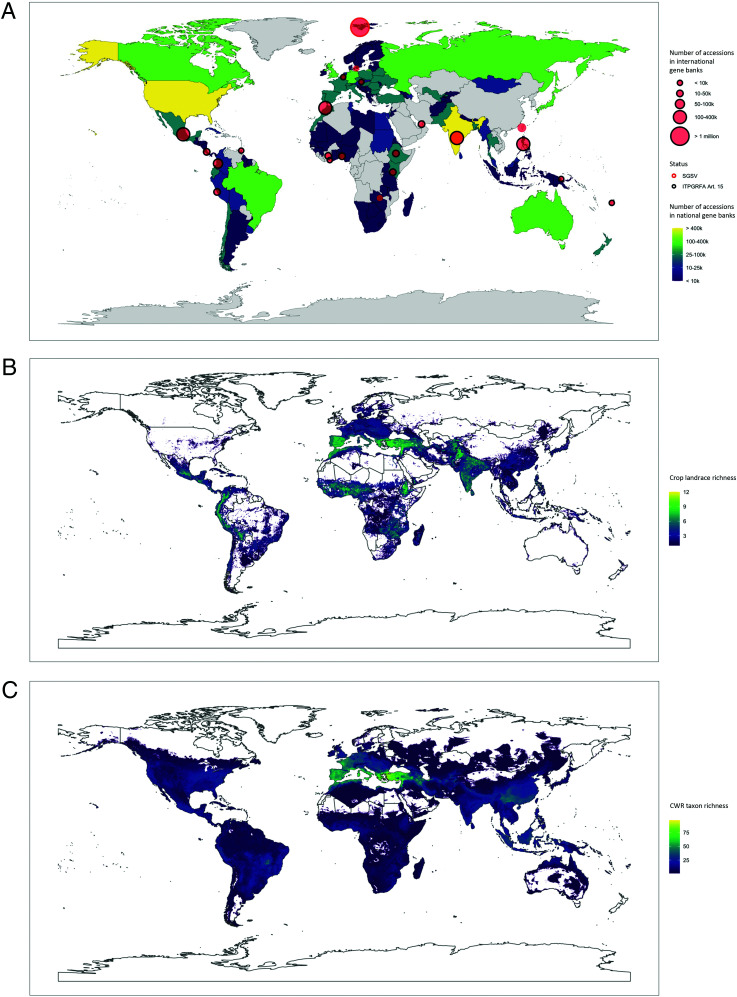
Fig. 1.
Comparison of plant genetic resource richness in ex situ conservation facilities as well as in situ in the field and in the wild. (A) The number of accessions in national genetic resource conservation facilities as reported to the FAO World Information and Early Warning System on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture (WIEWS) database (https://www.fao.org/wiews/en/) is shown in different colors. The geographic locations of international, including regional, gene banks around the world are indicated by circles. The size of the circles corresponds to the reported number of PGRFA accessions in international gene banks. Information on the holdings of the Svalbard Global Seed Vault (SGSV) was retrieved from the Seed Portal (https://seedvault.nordgen.org/), and information on Article 15 status under the Plant Treaty was retrieved from the Plant Treaty website (https://www.fao.org/plant-treaty/areas-of-work/the-multilateral-system/collections/en/). (B) Modeled crop landrace group richness of 25 major crops. Modified from ref. 3. (C) Modeled richness of 1,076 CWR taxa related to 81 crops. Modified from ref. 36.