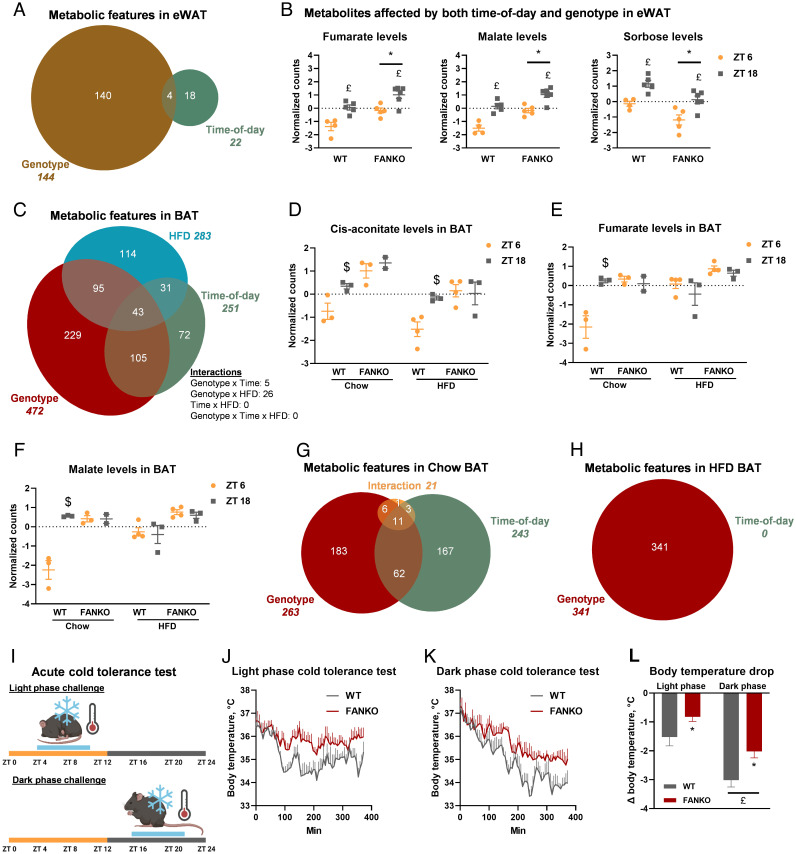
Fig. 4.
The effect of Nampt ablation on metabolite rhythmicity is tissue and diet dependent. Metabolomics analysis of eWAT from WT and FANKO mice harvested at ZT 6 and ZT 18 (n = 4 to 6). (A) Euler diagram of metabolic features in eWAT significantly affected by genotype, time-of-day, or an interaction between these two factors. (B) Metabolites affected by both genotype and time-of-day in eWAT. Metabolomics analysis of BAT of chow- and high-fat diet (HFD)-fed WT and FANKO mice harvested at ZT 6 and ZT 18 (n = 2 to 4). (C) Euler diagram of metabolic features significantly affected by genotype, time-of-day, and HFD as determined by three-way ANOVA. Day and night levels of (D) cis-aconitate, (E) fumarate, and (F) malate in BAT of WT and FANKO mice fed chow or HFD. (G) Euler diagram of metabolic features in BAT of chow-fed animals significantly affected by genotype, time-of-day, or an interaction between these two factors. (H) Euler diagram of metabolic features in BAT of HFD-fed animals significantly affected by genotype, time-of-day or an interaction between these two factors. (I) Schematic of acute cold tolerance test. (J) Light and (K) dark phase cold tolerance test. (L) Body temperature drop for the two cold tolerance tests. All metabolomics analyses were performed with FDR cutoff < 0.05. * denotes significantly difference between WT and FANKO. £ denotes significantly difference with time-of-day. $ denotes significant difference with time-of-day in WT at the same diet.