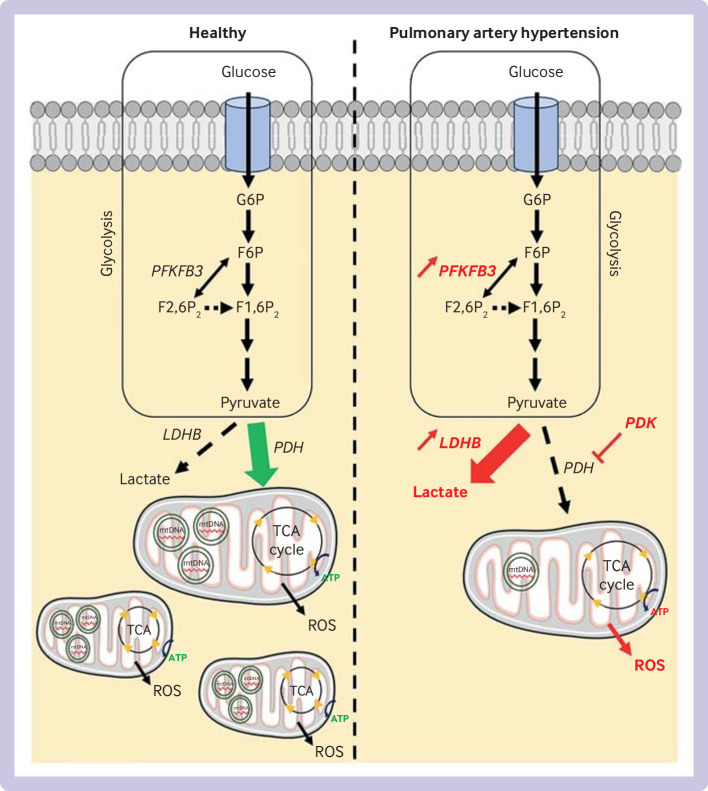
Figure 3.
Overview of major glycolytic and mitochondrial changes in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Glycolysis is upregulated in pulmonary arterial hypertension, and characterised by an increase in expression of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) and lactate dehydrogenase-B (LDHB) in lung cells. Upregulation of LDHB is associated with inhibition of pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK), leading to accumulation of lactate in cytoplasm and reduced mitochondrial biogenesis. Reduction in generation of ATP by tricarboxylic cycle (TCA) occurs in pulmonary vascular cells, associated with reduction in quantity of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and increase in production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Changes in fatty acid oxidation have not been fully elucidated. These abnormalities have been found in pulmonary artery endothelial cells, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells, and in the right ventricle. G6P=glucose 6-phosphate; F6P=fructose 6-phosphate; F2,6P2=fructose 2,6-bisphosphate; F1,6P2=fructose 1,6-bisphosphate