Fig. 10.
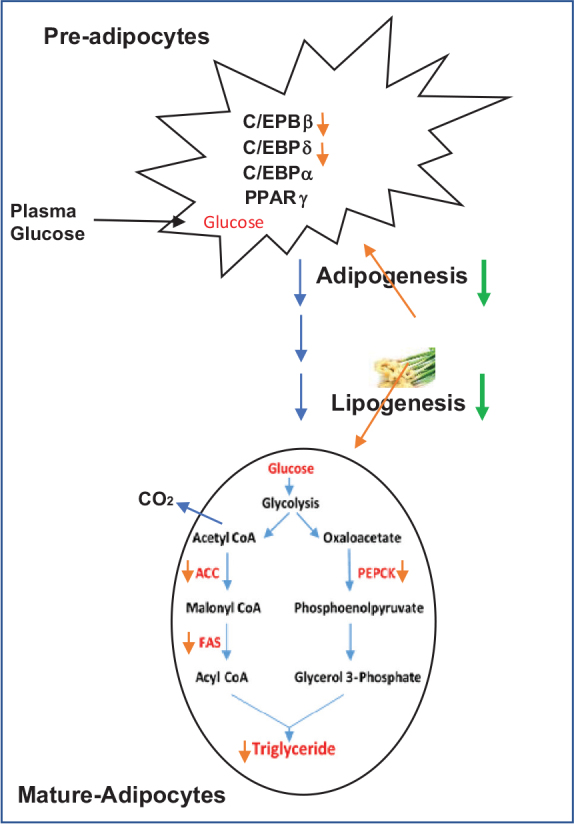
Potential targets of ginger on adipogenesis and lipogenesis to regulate obesity. Ginger can potentially inhibit adipogenesis by reducing the expression of C/EBPb and C/EBPd genes, consequently preventing adipocyte maturation. Ginger can also potentially inhibit the utilization of glucose into lipogenesis pathways by limiting the channeling of glucose carbon in fatty acid synthesis via inhibiting the expression of Acyl CoA Carboxylase (ACC) and Fatty Acid Synthase (FAS) and into glycerol production, and via inhibiting the expression of Phospho-Enol-Pyruvate Carboxy Kinase (PEPCK), which consequently inhibits triglyceride formation. The stimulated glucose uptake by ginger may be converted to CO2.
