Figure 1.
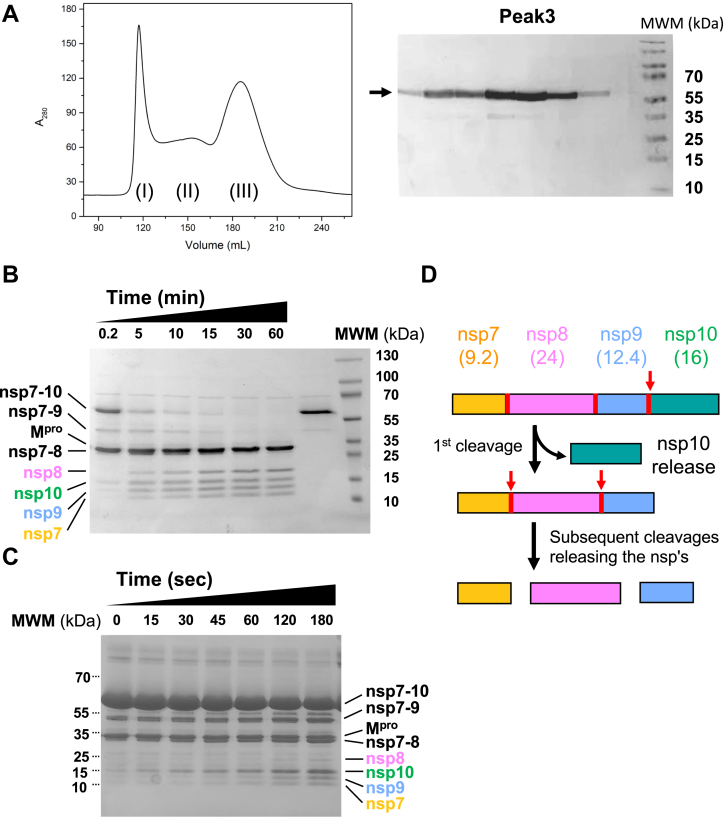
nsp7-10 polyprotein processing by Mpro.A, preparation of the nsp7-10 polyprotein. Different oligomers of nsp7-10 polyprotein (peaks I, II, and III) were separated by size-exclusion chromatography in the presence of 1 M NaCl in the purification buffer (left). Proteins in fraction III were analyzed by SDS‒PAGE (right). The molecular weight of the nsp7-10 polyprotein is 58.2 kDa. B, limited nsp7-10 polyprotein proteolysis by Mpro. Substrate (nsp7-10), products (nsp7, nsp8, nsp9, and nsp10), intermediates (nsp7-8, nsp7-9), and Mpro were separated by SDS‒PAGE and labeled. The time after mixing Mpro with nsp7-10 (1:1 ratio) is indicated above the lanes. C, limited nsp7-10 proteolysis assay under substrate excess conditions (Mpro:nsp7-10 = 1:4). D, schematic illustration of stepwise nsp7-10 polyprotein cleavage by Mpro. Nonstructural proteins within nsp7-10 and their molecular weights are indicated. Mpro recognition sites found between nsps are depicted as red lines, and the cleavage order is indicated by red arrows. Mpro, main protease.