Figure 7. Reactivation of endogenized viral elements in bat pluripotent stem cells.
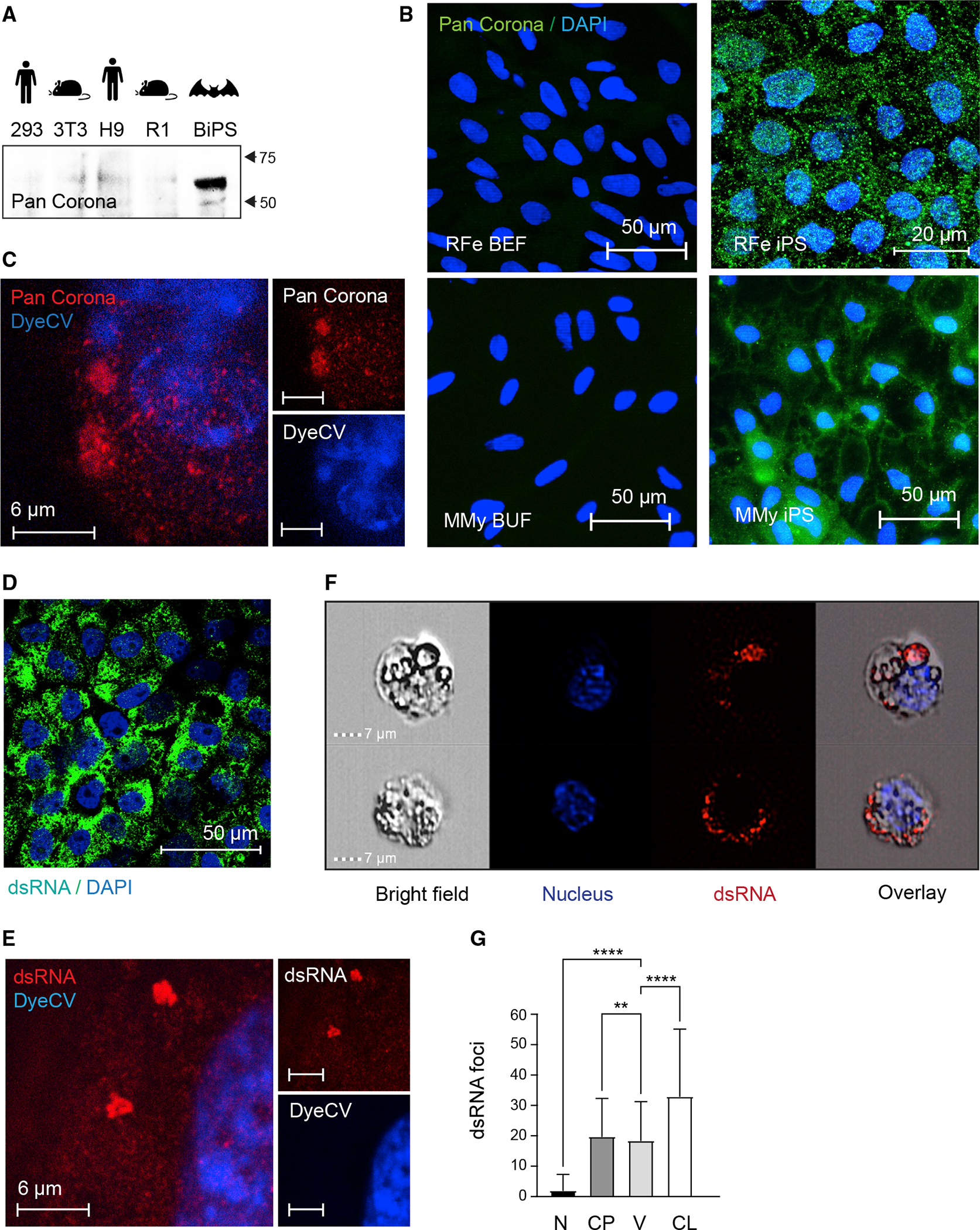
(A) Western blotting of protein lysates isolated from human 293FT and H9, mouse 3T3 and R1, and R. ferrumequinum BiPS cells with a pan coronavirus antibody known to be specific for the nucleocapsid; its reactivity includes, but might not be limited to, feline infectious peritonitis virus type 1 and 2, canine coronavirus (CCV), pig coronavirus transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV), and ferret coronavirus.
(B) Immunofluorescence images of R. ferrumequinum (RFe) bat embryonic fibroblasts (BEFs) and iPS cells from (top) and M. myotis (MMy) bat uropatagium fibroblasts (BUF) and iPS cells (bottom) after detection of the pan coronavirus antigen (green); DAPI (blue).
(C) Representative STED microscopy image of R. ferrumequinum iPS cells after detecting the Corona antigen as in (B) and DyeCycle Violet (DyeCV) nuclear counter stain (blue).
(D) Immunofluorescence images of R. ferrumequinum BiPS cells after detection of double-stranded RNA (green) characteristic of RNA viruses; DAPI (blue).
(E) Representative STED microscopy image of R. ferrumequinum iPS cells after immunofluorescence staining of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) as in (D).
(F) ImageStream analysis after immunofluorescence staining of BiPS cells as in (D and E). A brightfield image, DyeCycle Violet nuclear staining (blue), dsRNA staining (red), and an overlay is shown for each representative cell.
(G) Quantification of dsRNA foci by ImageStream in R. ferrumequinum iPS cells show in (F). Data are presented as mean +/− SD; n = 1,846 cells. **p < 0.01,****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. RFe, Rhinolophus ferrumequinum; BEF, bat embryonic fibroblasts; CP, cytoplasm; CL, cell; iPS, induced pluripotent stem cells; MMy, Myotis myotis; N, nucleus; V, vesicle; BUF, bat uropatagium fibroblasts.
See also Figures S4–S7 and Tables S5, S6, and S7.
