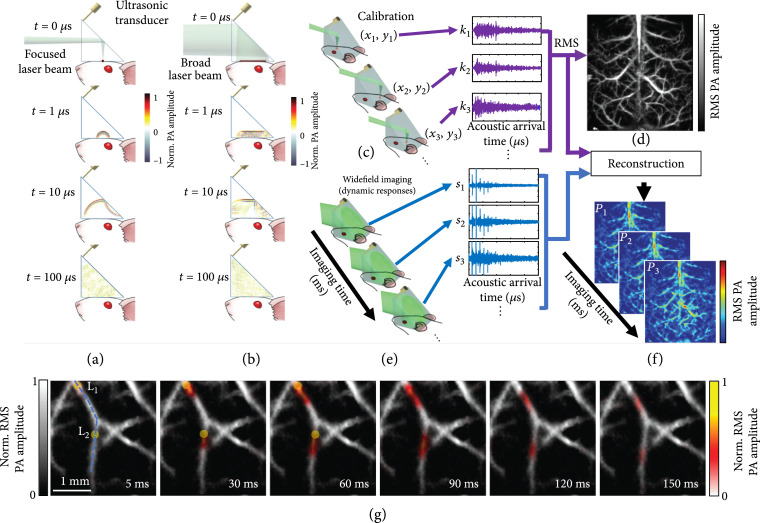
Figure 9.
Principles of PATER and representative images [100]. (a-f) Principles of PATER. (a) Simulation of acoustic propagation in the ER in calibration mode. Norm.: normalized. (b) Simulation of acoustic propagation in the ER in wide-field mode. (c) In the calibration mode, light is focused on each pixel to acquire the impulse response encoded by the ER, , and then raster scanned over the FOV. (d) Calibration image formed by computing the root-mean-squared amplitude of each received PA signal at every calibration position. (e) Snapshot wide-field imaging. A broad laser beam illuminates the entire FOV to acquire encoded signals, , which can be repeated for high-speed imaging. (f) Reconstructed wide-field images. The reconstruction algorithm uses calibrated impulse responses to decode the wide-field signals and then display wide-field images. (g) Monitoring of blood pulse wave propagation. Wide-field images at different time points illustrate the thermal wave propagation in the middle cerebral arteries. The yellow circles, labeled and , indicate the locations of the laser heating spots during wide-field measurement. The thermal wave signals are shown in color, and the background vessels are shown in gray.