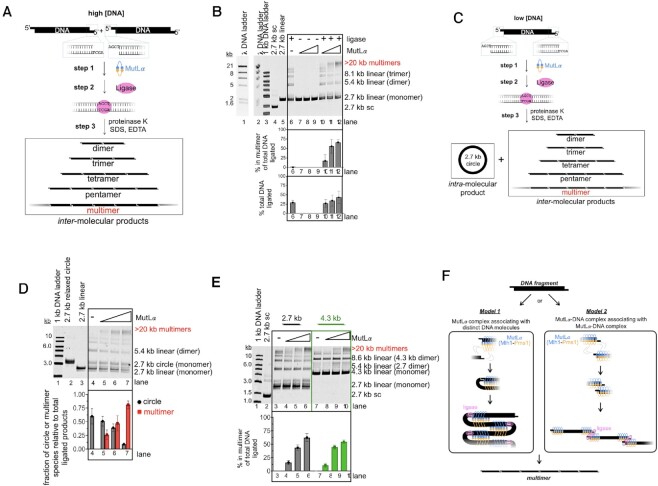
Figure 1.
MutLα complexes facilitate inter-molecular associations. (A) Schematic depicting ligation assays. 2.7 kb DNA is linearized with a restriction enzyme, creating ligatable ends. T4 DNA ligase is added at low concentrations so that inter-molecular products are preferentially created after MutLα is bound to DNA where indicated. (B) Ligation experiment using linearized 2.7 kb DNA with 5′ overhangs generated by HindIII restriction digest. Lanes 1 and 2 contain DNA markers generated by digesting lambda DNA (NEB) with HindIII. Lane 3 contains 1 kb ladder (NEB). Lanes 4 and 5 contain covalently closed, supercoiled (sc) circular 2.7 kb DNA and linear DNA starting material, respectively. Where +, T4 DNA ligase is added as indicated in the Materials and Methods. In lanes where a titration of MutLα is indicated the concentration of protein is 50, 150 and 300 nM. The amount of signal in the highest molecular weight band was quantified relative to the total amount of ligated product in each lane and the total amount of DNA ligated was quantified relative to total amount of DNA in lane. The average values for these are expressed in bar graph below the gel. The experiment was performed in triplicate and error bars represent standard deviations between experiments. (C) Schematic depicting ligation assay using low DNA concentrations where reformation of the circular intra-molecular product is preferred. (D) Top, Ligation assay using low DNA concentration (1.4 nM relative to 3.8 nM used in panels B and D). MutLα was titrated and lanes 5–7 contain 50, 150 and 300 nM, respectively. Bottom, graph depicts the amounts of DNA in each product relative to the total amount ligated. Number of replicates is n = 3. (E) Ligation assay using linearized 2.7 and 4.3 kb DNA with 5′-overhangs generated by HindIII. Lanes 4–6 and 8–10 are titrations containing 50, 150 and 300 nM MutLα.Number of replicates is n = 3. (F) Models for MutLα forming DNA multimers by promoting inter-molecular associations.