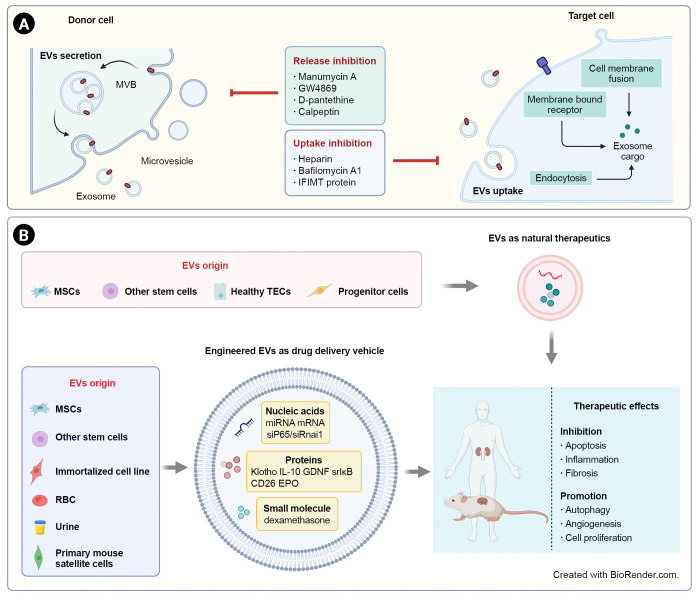
Figure 2. EV-based therapeutic strategies for renal fibrosis.
(A) Due to the pathological effects of EVs in renal inflammation and fibrosis, inhibition of EV secretion or uptake is a potential strategy for kidney diseases. (B) EVs derived from stem cells or healthy renal intrinsic cells could act as direct natural therapeutics. EVs can also be used as delivery vehicles for a variety of drugs, including nucleic acids, proteins, and small molecules. EV-based treatments have shown therapeutic effects on renal fibrosis through inhibition of apoptosis, inflammation, and fibrosis and promotion of autophagy, angiogenesis, and proliferation.
EVs, extracellular vesicles; EPO, erythropoietin; GDNF, glial-derived neurotrophic factor; IL, interleukin; miRNA, microRNA; mRNA, messenger RNA; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; MVB, multivesicular body; RBC, red blood cell; srIκB, super-repressor IκB; TECs, tubular epithelial cells.