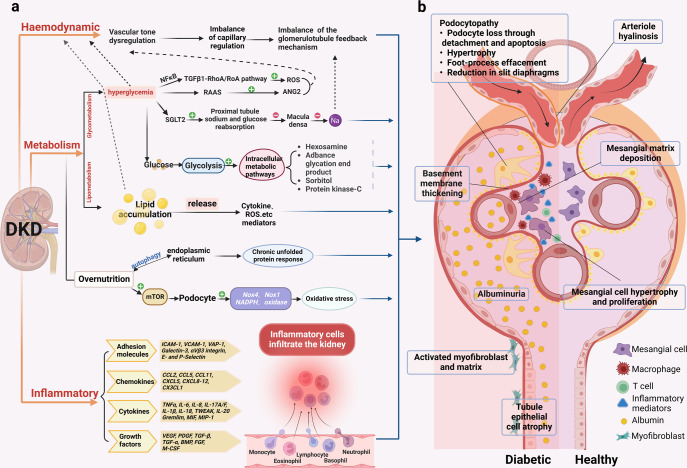
Fig. 4.
Pathology of the glomerulus and tubules in DKD. a The classical pathological mechanisms of DKD. It mainly includes hemodynamic, metabolic disturbances, and inflammation, which often interact with each other. (1). Hemodynamic disturbances lead to dysregulation of tubulobulbar feedback balance. (2). Metabolic disorders are crucial to the pathogenesis of DKD. Hyperglycemia affects pathways such as TGFβ1-RhoA/Roa pathway, RAAS, proximal tubular sodium and glucose reabsorption, and intracellular metabolism; abnormal lipid metabolism can affect the release of mediators such as cytokines and ROS; in the presence of nutrient overload in the organism, endoplasmic reticulum autophagy leads to a chronic unfolded protein response, and mTOR also disturbs the podocytes leading to oxidative stress. (3). Inflammation promotes the release of inflammatory mediators such as adhesion molecules, chemokines, cytokines, and growth factors, causing renal infiltration of inflammatory cells. b Schematic representation of the pathological damage of DKD. Differences in structural changes of glomeruli and tubules in the diabetic setting and in the healthy state. Diabetic glomerulopathy is characterized by arterial hyalinization, thylakoid stromal deposition, basement membrane thickening, glomerular thylakoid cell hypertrophy and proliferation, podocytosis, proteinuria, tubular epithelial atrophy, activated myofibroblasts, and stromal accumulation. NFκB nuclear factor kappa-B, TGFβ transforming growth factor-β, ROS reactive oxygen species, RAAS renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, ANG2 angiotensin II, SGLT2 sodium-dependent glucose transporters 2, mTOR mammalian target of rapamycin, NADPH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, NOX NADPH oxidase, ICAM-1 intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1, VCAM-1 vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, VAP-1 vascular adhesion protein-1, CCL CC chemokine ligand, CXCL C-X-C motif chemokine ligand, TNF tumor necrosis factor, IL interleukin, TWEAK tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis, MIF macrophage migration inhibitory factor, MIP-1 macrophage inflammatory protein-1, VEGF vascular endothelial growth factor, PDGF platelet-derived growth factor, BMP bone morphogenetic protein, FGF fibroblast growth factor, M-CSF macrophage colony-stimulating factor