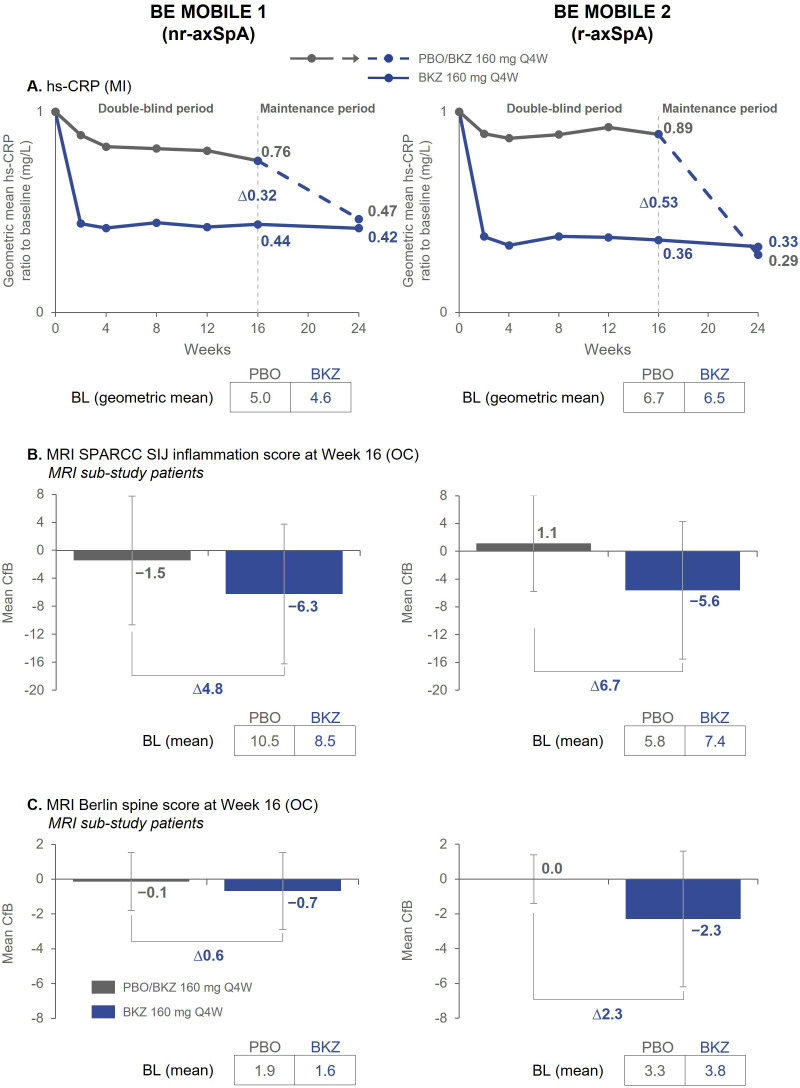
Figure 3.
Objective signs of inflammation. Randomised set. Exploratory endpoints. Error bars show SD. (A) n=128 (BKZ) and n=126 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 1, n=221 (BKZ) and n=111 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 2; (B) At BL, n=79 (BKZ) and n=68 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 1, n=83 (BKZ) and n=45 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 2. At week 16, n=77 (BKZ), n=60 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 1, n=79 (BKZ) and n=43 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 2; (C) At BL, n=75 (BKZ) and n=65 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 1, n=82 (BKZ) and n=45 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 2. At week 16, n=73 (BKZ) and n=58 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 1, n=79 (BKZ) and n=43 (PBO) in BE MOBILE 2. MRI Berlin spine score ranges from 0 to 69; lower scores indicate less spinal inflammation and negative changes represent improvements. MRI SPARCC SIJ inflammation scores range from 0 to 72; lower scores indicate less SIJ inflammation and negative changes represent improvements. BKZ, bimekizumab; BL, baseline; CfB, change from baseline; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; MI, multiple imputation; nr-axSpA, non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; OC, observed case; PBO, placebo; Q4W, every 4 weeks; r-axSpA, radiographic axial spondyloarthritis; SIJ, sacroiliac joint; SPARCC, Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada.