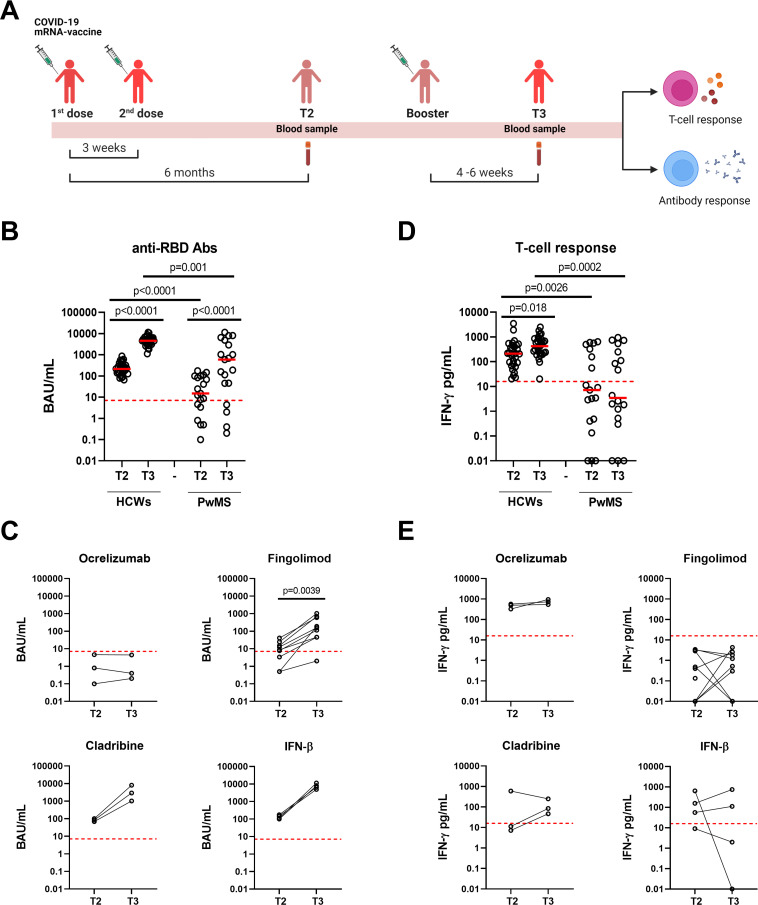
Figure 1.
Kinetic of the antibody and T-cell responses to COVID-19 vaccine in HCWs and PwMS. (A) Timeline of COVID-19 vaccination and study enrolment. For the analyses, blood samples of both HCWs and PwMS were collected after 6 months from the first vaccine dose (T2) and after 4–6 weeks from the booster dose (T3). Anti-RBD antibodies (B, C) and T-cell response (D, E) were evaluated in HCWs (n=30) and PwMS followed over time (n=19). (C, E) Antibody and T-cell responses were stratified according to DMTs: ocrelizumab (n=3), fingolimod (n=9), cladribine (n=3) and IFN-β (n=4). (B, C) Anti-RBD-IgG were measured in sera samples and expressed as binding antibody units (BAU)/mL. The cut-off was set at 7.1 BAU/mL (red dashed line). (D, E) For T-cell response, IFN-γ levels were quantified using an automatic ELISA and reported after subtracting the unstimulated control value. The cut-off was set at 16 pg/mL (red dashed lines). Data were analysed using Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon matched pairs signed rank test and p values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. Each dot represents a different individual. Abs, antibodies; BAU, binding antibody units; DMTs, disease modifying therapies; HCWs, healthcare workers; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; IFN-β, interferon beta; PwMS, patients with multiple sclerosis; RBD, receptor-binding domain.