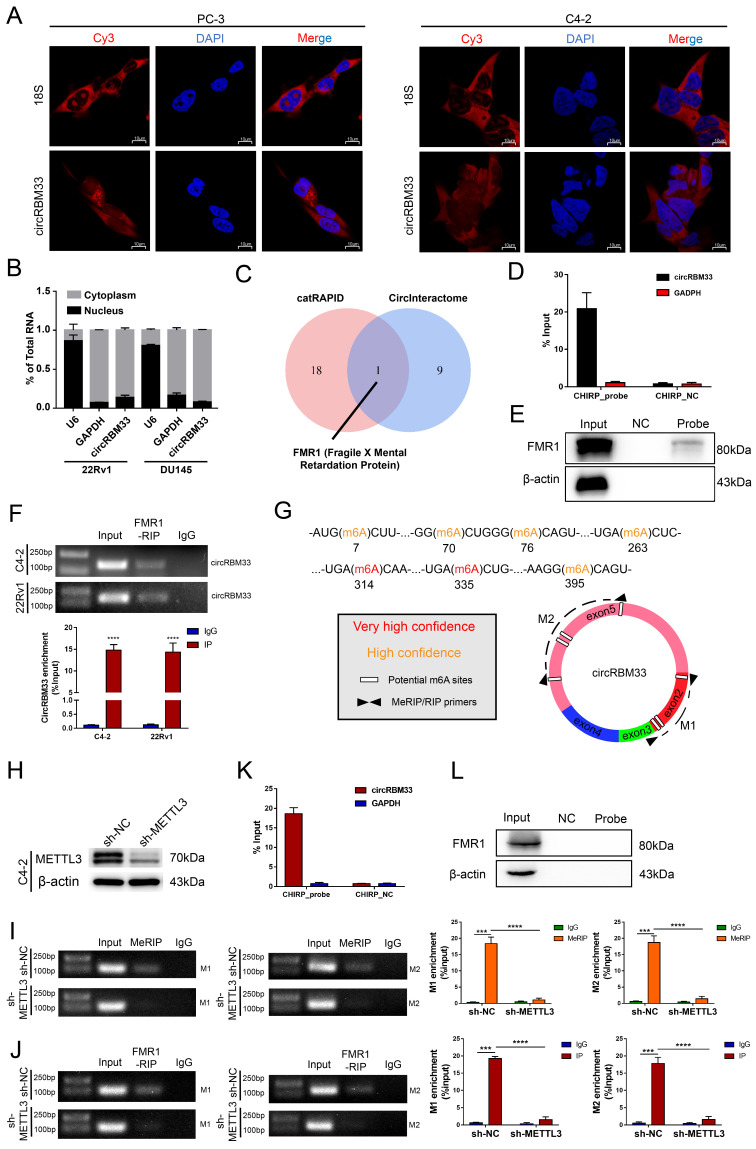
Figure 3.
CircRBM33 interacts with FMR1 in m6A-mediated manner. (A) FISH assays show the subcellular localization of circRBM33 in PCa cells (PC-3 and C4-2) with 18S acting as a positive control. (B) The nuclear and cytoplasmic extraction experiments show the nucleus/cytoplasm proportion of circRBM33. (C) The protein that overlapped between the catRAPID database and the CircInteractome database. (D) qRT-PCR confirms the enrichment of the ChIRP probe designed to circRBM33. (E) WB confirms the pulldown of FMR1 by the ChIRP probe. (F) The RIP experiments show the enrichment of circRBM33 by FMR1. (G) A schematic representation of the potential m6A-modified sites in circRBM33. (H) Wb confirms the transfection efficiency of shRNA to METTL3. (I) MeRIP assay confirms the enrichment of circRBM33 by m6A in METTL3-knockdown and control groups. (J) FMR1-RIP assay detects the enrichment of circRBM33 by FMR1 in METTL3-knockdown and control groups. (K) D) qRT-PCR confirms the enrichment of the ChIRP probe designed to circRBM33 in METTL3-knockdown groups. (L) WB confirms the pulldown of FMR1 by the ChIRP probe under the downregulation of METTL3.