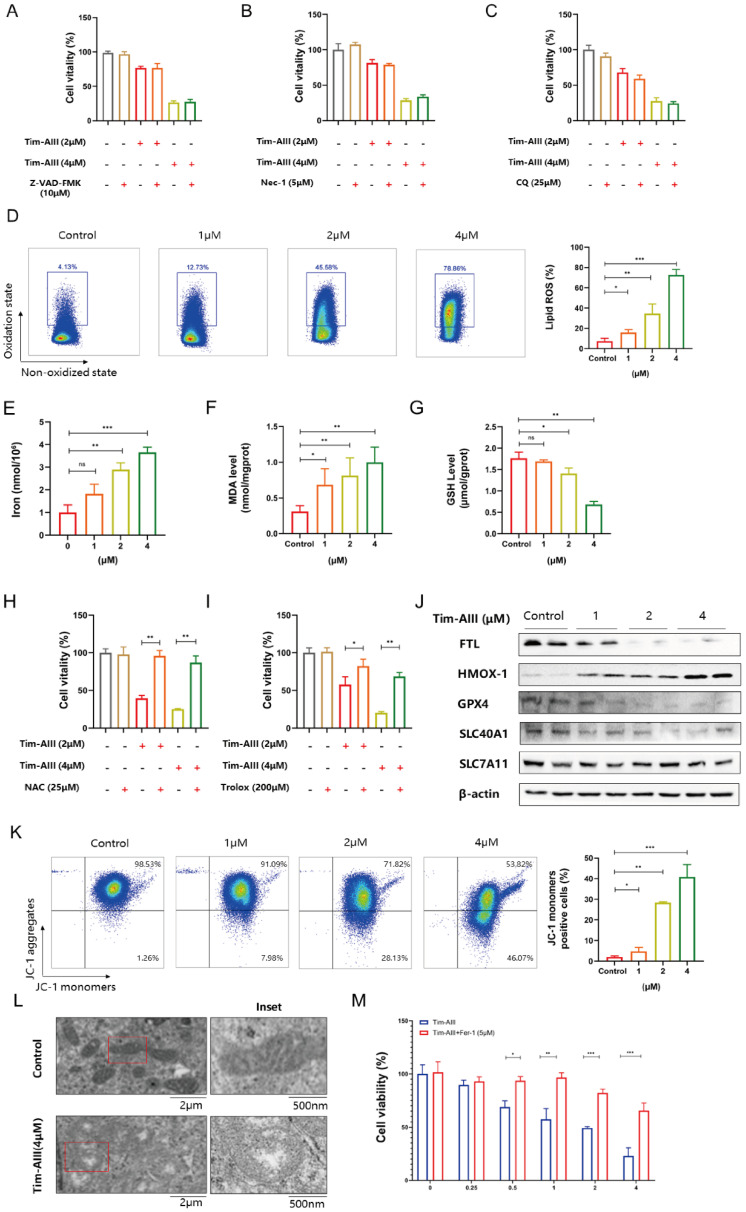
Figure 3.
Tim-AIII-induced cell death is mainly caused by ferroptosis in H1299 cells. A-C H1299 cells were cotreated with Tim-AIII with or without Z-VAD-FMK, Nec-1 and CQ for 48 h, and cell vitality was assayed by the CCK-8 assay. D The lipid ROS level was analyzed using a flow cytometer after treatment with Tim-AIII for 48 h in H1299 cells. E The intracellular iron level after Tim-AIII treatment for 48 h in H1299 cells. F Intracellular MDA levels after treatment with Tim-AIII for 48 h in H1299 cells. G The intracellular GSH levels after Tim-AIII treatment for 48 h in H1299 cells. H-I H1299 cells were co-treated with Tim-AIII with or without the ROS inhibitor NAC and trolox for 48 h, and cell viability was assessed by CCK-8. J The expression of several key ferroptosis regulators, such as FLT, HMOX-1, GPX4, SLC40A1, SLC7A11, was examined by WB in H1299 cells. K Representative results of flow cytometry and quantification of mitochondrial membrane potential (JC-1 monomers) after treatment with Tim-AIII for 48 h in H1299 cells. L TME was used to observe mitochondrion in H1299 cells. M H1299 cells were cotreated with Tim-AIII with or without Fer-1 for 48 h, and cell vitality was assayed by the CCK-8 assay. Quantitative data were presented as mean ± SD. *p< 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.