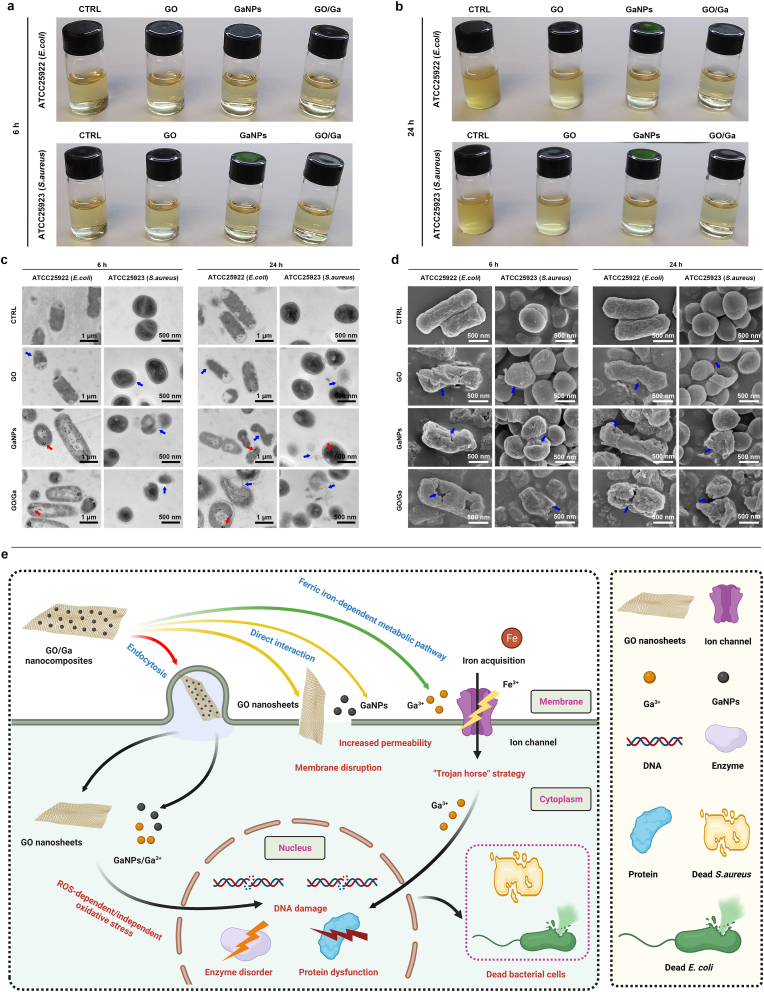
Fig. 3.
Morphological analysis of bacteria by microscopy and potential antibacterial mechanisms. (a, b) The appearance of culture medium containing different nanomaterials and tested bacterial strains after 6 and 24 h incubation, respectively. (c) TEM images of E. coli and S. aureus treated with different nanomaterials. (d) SEM images of E. coli and S. aureus treated with different nanomaterials. (e) Schematic illustration and summary of potential bacterium inactivation mechanisms via interaction with the GO/Ga nanocomposites according to the results of our study and previous reported findings (Created with BioRender.com). Marked red arrows denote the cellular uptake of released Ga nanoparticles, and blue arrows denote dying or dead cells with destroyed bacterial membrane.