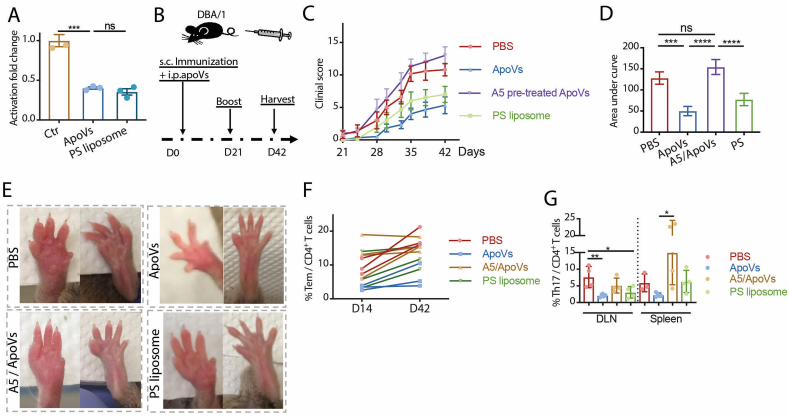
Fig. 6.
ApoVs prevent T cell activation in murine arthritis via phosphatidylserine. (A) Activation fold change of naïve CD4+ T cells stimulated in the presence of PBS (Ctr), 0.2 x apoVs (ApoVs) or 0.2 x phosphatidylserine (PS) liposomes. N = 3 per group. (B) Scheme of D0 systemic apoV injection in collagen-induced arthritic DBA/1 (CIA) mice. (C, D) Comparison of clinical scores in mice receiving D0 PBS, apoVs, A5 pre-treated apoVs, or PS liposomes measured every 3 days from D21 until the endpoint. N = 5–6 per group. (E) Representative images of arthritic front and hind paws of CIA mice receiving D0 PBS, apoVs, A5 pre-treated apoVs, or PS liposomes at the time of harvest. (F) Frequency of Tem CD4+ T cells in circulation of CIA mice receiving D0 PBS, apoVs, A5 pre-treated apoVs, or PS liposomes at D14 and D42. N = 3–4 per group. (G) Frequency of Th17 cells from draining lymph nodes (DLN) and spleen of CIA mice receiving D0 PBS, apoVs, A5 pre-treated apoVs, or PS liposomes. N = 3–5 per group. Kruskal-Wallis test and ANOVA was used for comparison among three groups when appropriate. Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation. ns, not significant. *, p < 0.05. **, p < 0.01. ***, p < 0.001. ****, p < 0.0001.