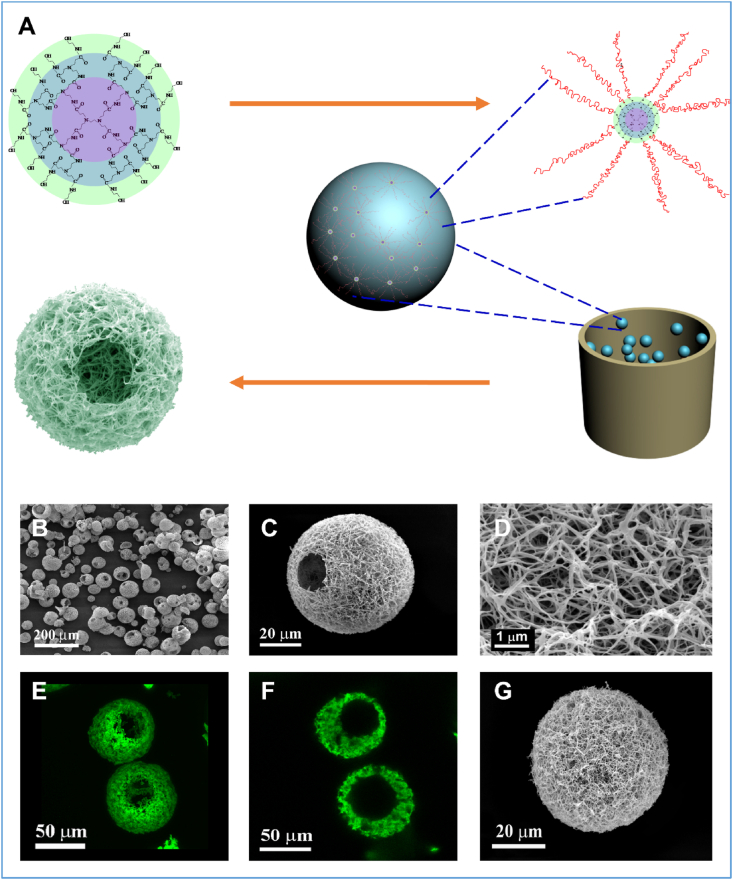
Fig. 4.
Fabrication of nanofibrous hollow microspheres. (A) Schematic illustration of the nanofibrous hollow microsphere formation. (B) The SEM image of nanofibrous hollow microspheres fabricated, showing open holes on the shell. (C) SEM image of a representative nanofibrous hollow microsphere, showing the nanofibrous architecture and a hole of approximately 20 μm on the microsphere shell. (D) A high-magnification image of the microsphere in (C), showing the nanofibers. (E) A 3D reconstruction of nanofibrous hollow microspheres from confocal image stacks. (F) A 2D cross-section confocal image of the nanofibrous hollow microspheres, confirming the hollow structure of the microsphere. (G), SEM image of a representative nanofibrous microsphere, showing the nanofibrous architecture on the microsphere surface. (H) SEM image of a representative solid-interior microsphere, showing the smooth surface of the microsphere. Adapted from Ref. [88], copyright 2011 Macmillan Publishers Limited.