Fig. 1.
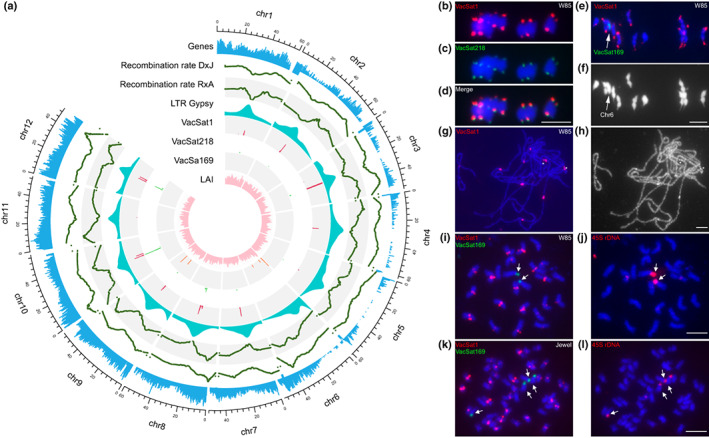
Chromosomal features of Vaccinium caesariense W85 genome (2n = 2x = 24) and representative V. corymbosum tetraploid blueberry cultivars (2n = 4x = 48). (a) Circular multi‐track plot illustrating the following chromosomal features: gene density, LTR/gypsy density, satellite repeat VacSat1, VacSat218 and VacSat169 and genome wide recombination rates estimated from two mapping populations (DS × J and R × A). The density of each feature was estimated considering a 200 kb window of W85_v2 genome assembly p0; b–l) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) of satellite repeats and 45S rDNA on the chromosomes of W85 (2n = 2x = 24) and Jewel (2n = 4x = 48). (b–d) Distribution of VacSat1 (b, red signals) and VacSat218 (c, green signals) on meiotic metaphase I chromosomes (in blue) of W85; (d) image merged from (b) and (c). (e, f) Localization of VacSat1 (red) and VacSat169 (green, arrow) on W85 meiotic metaphase I chromosomes (blue); (f) the chromosomes in (e) shown in gray scale to better visualize the location of VacSat1 on stretched terminal regions of most bivalents. (g) Localization of VacSat1 (red) on W85 meiotic pachytene chromosomes; (h) pachytene chromosomes in (g) shown in gray scale to enhance the visualization of the heterochromatic domains overlapped by VacSat1. Two chromosomes each had two adjacent VacSat1 signals separated by a short gap on unlabeled chromatin (asterisks). (i) Distribution of VacSat1 (red) and VacSat169 (green) on mitotic metaphase chromosomes (blue) of W85; VacSat169 is located on two chromosomes lacking VacSat1 signals (arrows); (j) the same chromosome plate used in (i) hybridized with 45S rDNA (red, arrows). (k) Localization of VacSat1 (red) and VacSat169 (green) on mitotic metaphase chromosomes of Jewel (2n = 4x = 48); VacSat169 is located on four chromosomes lacking VacSat1 signals (arrows); (l) the same chromosome plate used in (k) hybridized with 45S rDNA (red, arrows). Bar, 5 μm.
