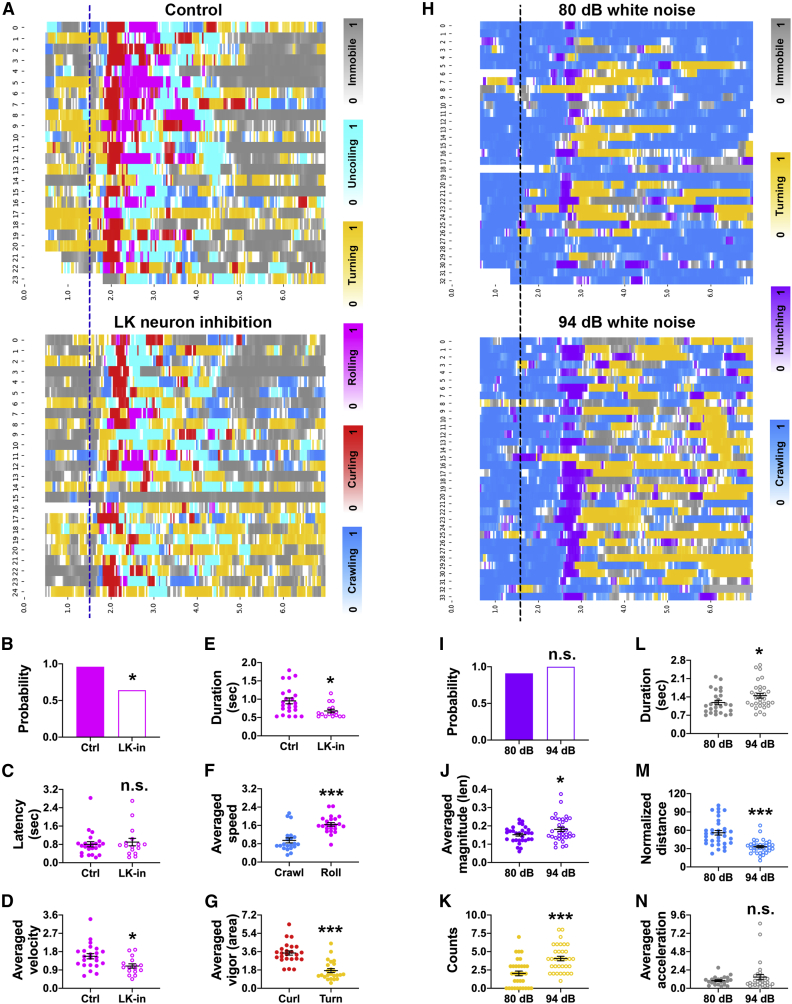
Figure 5.
The Quantifier captures subtle changes in the behavior of Drosophila larvae
(A and H) Raster plots showing the frame-wise categorizations by: (A) LarvaN on control (w; LK-GAL4/+; TrpA1-QF, QUAS-ChR2T159C, UAS-jRCaMP1b/+) and LK neuron inhibition (w; LK-GAL4/+; TrpA1-QF, QUAS-ChR2T159C, UAS-GtACR1/+) groups after nociceptors were optogenetically activated (blue dashed line indicates the stimulation onset); (H) LarvaMechanosensor_Topview_30fps on larvae (Canton S) under different intensities of sound stimuli (black dashed line indicates the stimulation onset). Color bars: behavioral categories (color intensities indicate the behavioral probabilities). The x axis represents the time and y axis represents the larval IDs.
(B–G) Parameters calculated by the Quantifier for different behaviors elicited by optogenetic activation of nociceptors. The colors match those for behaviors shown in (A). Data in (F) and (G) are from the control group in (A).
(I–N) Parameters calculated by the Quantifier for different behaviors elicited by sound stimulation. The colors match those in (H). Probability in (B) and (I) is the fraction of responders (behavioral count > 0) in total animals. n.s., p > 0.05; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗∗p < 0.001 (Fisher exact test for B and I; unpaired t test for C–G and J–N). Error bars represent standard error of the mean.