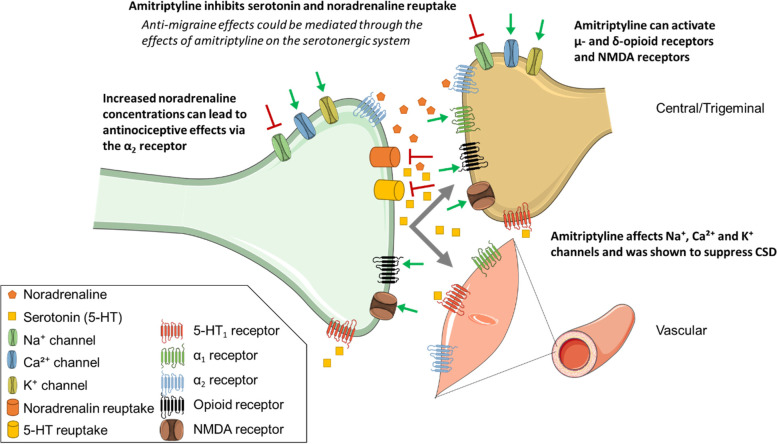
Fig. 1.
Potential mechanisms of action for the anti-migraine effect of the tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline. Amitriptyline inhibits the uptake of serotonin and noradrenaline in the synaptic cleft, and possibly exerts its antimigraine effects by affecting serotonergic transmission or through antinociceptive effects via activation of the α2 adrenoreceptor [8]. In addition, tricyclic antidepressants affect sodium [14] calcium [10] and potassium [11] channels, exert an effect on adrenergic α1, NMDA and opioid receptors [12] and suppress cortical spreading depression (CSD), which could be underlying migraine aura [13]