Table 3.
Results of Applying the 3 Strategies to Data Generated Under Different Scenarios, With 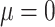 and
and 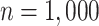
| Strategy |
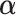 a
a
|
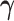
|
Bias | Coverage | RMSE | MCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Missingness | ||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.00 | 95.0 | 0.00 | 0.01 |
| MCAR | ||||||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.01 | 95.0 | 0.24 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.01 | 94.6 | 0.14 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | 0.00 | 97.9 | 0.22 | 0.01 | ||
| MAR | ||||||
| 1 | −0.4 | 0 | −0.09 | 93.2 | 0.26 | 0.01 |
| 2 | −0.07 | 91.7 | 0.17 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | −0.01 | 97.9 | 0.24 | 0.01 | ||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0 | 0.05 | 94.3 | 0.22 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.07 | 92.8 | 0.14 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | 0.00 | 97.6 | 0.22 | 0.01 | ||
| MNAR | ||||||
| 1 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.16 | 86.3 | 0.26 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.17 | 73.0 | 0.22 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | −0.00 | 97.3 | 0.20 | 0.01 | ||
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.12 | 90.4 | 0.24 | 0.01 |
| 2 | 0.12 | 85.3 | 0.17 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | 0.00 | 97.6 | 0.22 | 0.01 | ||
| 1 | −0.2 | −0.2 | −0.17 | 90.0 | 0.30 | 0.01 |
| 2 | −0.15 | 83.3 | 0.22 | 0.00 | ||
| 3 | 0.00 | 98.2 | 0.07 | 0.01 | ||
| 1 | −0.4 | −0.4 | −0.33 | 75.3 | 0.42 | 0.01 |
| 2 | −0.31 | 53.4 | 0.34 | 0.01 | ||
| 3 | 0.01 | 98.7 | 0.17 | 0.01 | ||
Abbreviations: MAR, missing at random; MCAR, missing completely at random; MCE, Monte Carlo error; MNAR, missing not at random; RMSE, root mean square error; 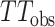 , target trial emulated from observed data; TTtrue, the full eligibility target trial, containing all those who are eligible.
, target trial emulated from observed data; TTtrue, the full eligibility target trial, containing all those who are eligible.
a Average size of 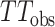 for the 7 settings of
for the 7 settings of 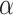 and
and 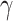 are n = 250, 228, 271, 328, 294, 206, and 172 respectively. Average size of
are n = 250, 228, 271, 328, 294, 206, and 172 respectively. Average size of 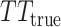 is 500. Note that the average causal effect
is 500. Note that the average causal effect 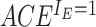 was calculated from a single simulation with
was calculated from a single simulation with 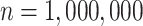 and was estimated at 2.386.
and was estimated at 2.386.
